
What is a Frequency Inverter? A Complete Guide to How It
4 days ago · A frequency inverter is an electronic device that converts the fixed frequency and fixed voltage from your electrical supply (e.g.,50Hz or 60Hz,240V or 480V)into a variable

Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
Oct 1, 2024 · In most regions, the standard inverter frequency for AC power systems is 50 or 60 Hz, representing the number of complete cycles per second. This inverter frequency is

Frequency inverter
3 days ago · Frequency inverter A frequency inverter is an electronic device which enables the conversion of an electrical variable ''current''. In this case, the frequency inverter transforms an

Understanding Variable Voltage Variable Frequency Inverters
May 13, 2024 · Choosing the Right Variable Voltage Variable Frequency Inverter for Your Needs Selecting the appropriate VVVF inverter for your application involves considering factors such
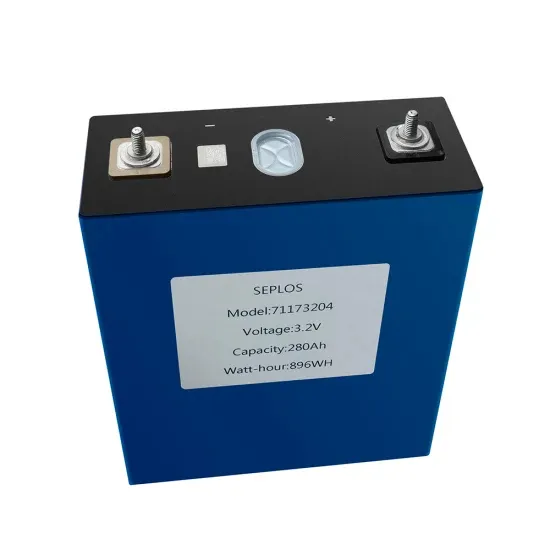

Understanding Frequency Inverters: A Comprehensive Guide
Feb 23, 2025 · When selecting a frequency inverter, consider the following factors: Power Requirements: Determine the voltage and wattage needed for your application. Load Type:
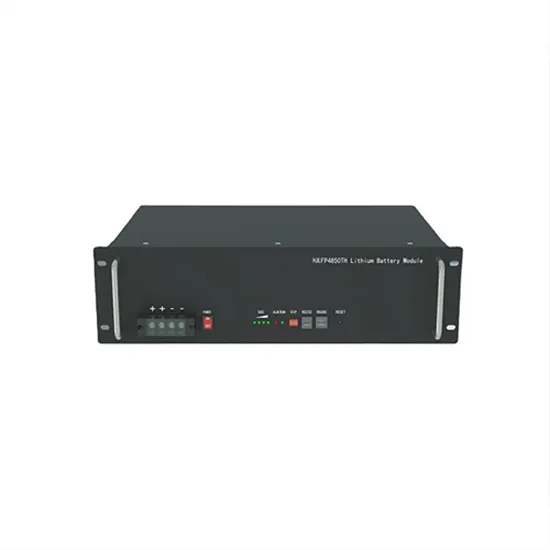

What is Frequency inverter?
The frequency inverter acts as a barrier in between all input voltage disturbances like harmonics, ripples, sags, surges, etc., and obstructs them from entering the motor. A resistive load can be

Voltage Control Methods of Inverter – PWM
Feb 12, 2022 · The voltage control is primarily achieved by varying the firing angle of the ac voltage controller that feeds the ac load. In this method, there is a

Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions
Dec 11, 2023 · Frequency inverter relies on the internal IGBT to adjust the voltage and frequency of the output power supply, according to the actual needs of the
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They
Dec 17, 2019 · Key learnings: Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for

Mastering Inverter Switching Frequencies: A
Apr 25, 2024 · The switching frequency of inverters in electric motor applications is critically controlled to optimize performance, efficiency, and minimize noise

Frequency Converter vs Inverter
Oct 22, 2024 · Electric Vehicles: In electric vehicles (EVs), inverters convert the DC power from the vehicle''s battery into AC power to drive the electric motor. How to Choose Between a

What is a Frequency Inverter and Why is it So Widely Used?
Apr 27, 2025 · A frequency inverter, commonly referred to simply as an inverter, modifies the frequency and voltage of an electrical power supply. Typically starting with a fixed - frequency

Frequency inverter design
Sep 5, 2018 · Gozuk inverters are suitable in the fields of power, iron and steel, HVAC, oil, mine, construction, etc for the high-voltage motor''s speed adjustment, energy saving, soft starting

6 FAQs about [Inverter voltage of power frequency inverter]
What is a frequency inverter?
Frequency inverters are electronic devices that create an AC voltage with variable frequency from an AC voltage with fixed frequency (e.g. 50 Hz). They are usually installed between the supply network and an electric motor so that its speed can be controlled steplessly and precisely and so that its energy consumption can be optimised.
What is AC inverter frequency?
1. What is the frequency of AC inverter? An AC inverter frequency refers to the number of power signal fluctuations, typically measured in Hertz (Hz). In most regions, the standard inverter frequency for AC power systems is 50 or 60 Hz, representing the number of complete cycles per second.
What are the components of a frequency inverter?
Frequency inverters are made up of the following main assemblies: The rectifier converts the AC voltage on the input side into DC voltage. The electrical components needed for this are known as uncontrolled or controlled bridges, such as thyristors or transistors.
What is a PWM in a frequency inverter?
PWM: A frequency inverter control scheme in which a constant dc voltage is used to reconstruct a pseudo ac voltage waveform using a set of six power switches, usually IGBTs. Varying the width of the fixed-amplitude pulses controls effective voltage.
How does an inverter control a motor?
An inverter uses this feature to freely control the speed and torque of a motor. This type of control, in which the frequency and voltage are freely set, is called pulse width modulation, or PWM. The inverter first converts the input AC power to DC power and again creates AC power from the converted DC power using PWM control.
How does inverter speed regulation work?
Inverter speed regulation is achieved by changing the frequency of the power supply to the stator winding of the motor. First, the rectifier section converts the AC power supply to DC power. This usually involves a rectifier bridge, which converts the AC voltage to DC voltage.
Learn More
- Dual voltage power frequency inverter
- What is the best voltage for a power frequency inverter
- Inverter variable frequency motor rated voltage
- Power frequency inverter connected to 220v to charge the battery
- Power frequency inverter off-grid
- How many watts is suitable for a 60V power frequency inverter
- Seoul power frequency isolation 50kw inverter
- Assembly of high power industrial frequency inverter
- High frequency inverter post-stage voltage stabilization components
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
