
48V Inverter: The Ultimate Guide to Efficient and Scalable Power
May 19, 2025 · Solar panels and batteries store power as DC, but your lights, TV, refrigerator, and power tools use AC – usually 110V or 220V, depending on your country. The inverter uses a

(a) Can Fatima also charge the battery of a phone by
Oct 30, 2023 · Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow. For most mobile devices, the voltage to recharge the battery is typically 5 volts of direct current. In India,

Can You Charge a Battery While Using an Inverter?
It is safe to charge a battery while using an inverter, and it benefits both because this reduces heat and the amps drawn. If you are using solar panels to charge the battery there is no

12V Battery to 220V Power Inverter charge controller
Jun 16, 2025 · A power inverter converts DC power or direct current to standard AC power or alternating current. The following schematic shows a 12V power inverter Circuit Diagram.

Can An Inverter Charge A Battery? Understanding Its Role In Charging
Feb 2, 2025 · Yes, an inverter can charge a battery when shore power is available. It converts AC power from shore power into a suitable form for your equipment. At the same time, it charges

AC-coupling Enphase IQ Microinverters with Victron
2 Introduction to AC-coupled systems In AC-coupled systems, IQ Series Microinverters and battery inverters are connected to a main AC line, where PV power is first used to power the

What is a Battery Inverter? A Comprehensive
Sep 5, 2024 · At its heart, a battery inverter is an electronic device that transforms direct current (DC) electricity, typically stored in a battery, into alternating
Can An Inverter Charge A Battery? Understanding Its Role In Charging
Feb 2, 2025 · When connected to a battery, the inverter-charger will regulate the charging process, often featuring multiple charging stages. This ensures the battery is charged

How To Charge Inverter Battery | Tips & Charging Time
Always use insulated tools to adjust the connections, ensuring your safety throughout the process. Before turning on the inverter to begin charging, double-check all connections. Ensuring

4000W Pure Sine Wave Inverter With UPS Battery Charger
Feb 19, 2025 · Power Up with 4000W Pure Sine Wave Power Inverter With Ups Battery Charger. Convert 12V 24V to 220V - 230V. Battery Charging AC Converter. Enjoy Free Shipping - Get

Can I Use Inverter While Charging Battery
May 7, 2025 · Yes, you can use an inverter while charging a battery, but it must be done with proper precautions and the right setup. Have you ever found yourself wondering whether it''s

6 FAQs about [Power frequency inverter connected to 220v to charge the battery]
Can You charge a battery while connected to an inverter?
Charging Battery While Connected To Inverter - Solar Panel Installation, Mounting, Settings, and Repair. There are two scenarios to consider when charging the battery while the inverter generates alternating current to the loads connected to the inverter.
Can a solar panel charge a battery with an inverter?
There are two scenarios to consider when charging the battery while the inverter generates alternating current to the loads connected to the inverter. A solar panel array can charge the battery via a charge controller, or the battery can be charged by a battery charger connected to the grid.
Can a battery charger overheat while using an inverter?
The inverter will stop working when the battery has reached its disconnect state of charge. Charging the battery from grid AC while using the inverter to generate AC to power the connected devices is possible. Still, caution should be taken not to allow the charger to overheat. Let’s consider all the possible permutations:
How does a power inverter get its energy?
As we dive into power source options and using a battery charger, it’s important to understand how the power inverter gets its energy. Most inverter set-ups have an inverter (converts 12 Volt DC power to 120 Volt AC power) and a power source (usually a single battery or battery bank). Inverter uses the battery to generate AC power.
How does an inverter/charger work?
An inverter simply converts DC (battery) power into AC power and then passes it along to connected equipment. An inverter/charger does the same thing, except that it is connected to an AC power source to continuously charge the batteries when AC utility power is available.
How many watts can a 500W Inverter Supply to a 12V battery?
(Explained With Examples) Assume you have a 500W inverter connected to a 105 Ah 12V battery, and the inverter supplies the maximum 400W to the AC-powered devices (400W/120V=3.33A). The battery can supply this 3.33A of 120V AC for a total of 15.76 hours before the battery state of charge reaches the cutoff level of 50%.
Learn More
- Can the UPS inverter be connected to the power supply to charge the battery
- Power battery conversion 220v inverter
- Base station lithium battery energy storage 15kw inverter power supply
- Is lithium battery plus inverter a mobile power supply
- 1kW high frequency inverter power consumption
- Inverter output frequency and power
- Can solar lights be connected to 220V lighting power
- 5kva high frequency power inverter
- Dual voltage power frequency inverter
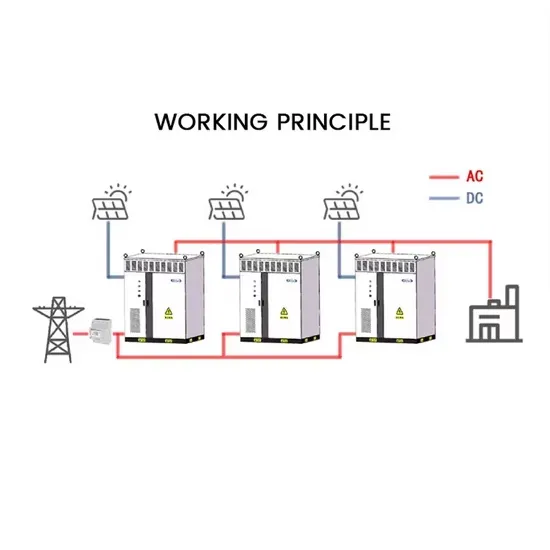
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
