
Frequency Shift Power Control
Aug 17, 2025 · The system diagram of Sungrow''s FSPC solution is showed in Fig-1, the PV inverter should be connected to the backup port of the hybrid inverter. In stand-alone grid

Synchronization of the solar inverter with the grid
Jan 29, 2025 · Use power quality monitoring equipment to verify that the output of the inverter is within the required limits for voltage, frequency, and harmonic

Inverter | Efficiency & Output Waveform
Inverter is a power device that converts direct current into alternating current, widely used in fields such as solar power generation, wind power generation, and uninterruptible power supply. The

What is a Frequency Inverter? A Complete Guide to How It
4 days ago · A frequency inverter is an electronic device that converts the fixed frequency and fixed voltage from your electrical supply (e.g.,50Hz or 60Hz,240V or 480V)into a variable

Everything You Need to Know About the Split Phase Inverter
Mar 13, 2025 · Power Rating: Ensure the inverter''s power rating is sufficient, to handle your total load power, considering starting power and power factor. Output Voltage and Frequency:

inverter output frequency
May 29, 2019 · inverter output frequency I''m using US power (230v @60hz) and I plan to install a quattro 230v 5k with my 24v battery. Question is, even if I''m supplying 60hz to the

800VA Pure Sine Wave Inverter''s Reference Design
Apr 1, 2023 · The pure Sine Wave inverter has various applications because of its key advantages such as operation with very low harmonic distortion and clean power like utility-supplied

CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_2
Mar 31, 2019 · An inverter uses this feature to freely control the speed and torque of a motor. This type of control, in which the frequency and voltage are freely set, is called pulse width

Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions
Dec 11, 2023 · The frequency inverter is a power control equipment that applies frequency conversion technology and microelectronics technology to control

Frequency Converter vs Inverter
Oct 22, 2024 · How to Choose Between a Frequency Converter and an Inverter When deciding between a frequency converter and an inverter, the most important factor is the nature of the

Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions
Dec 11, 2023 · A frequency inverter is a device that converts industrial frequency power supply (50Hz or 60Hz) into AC power supply of various frequencies to
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They
Dec 17, 2019 · Key learnings: Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for

Three-phase inverter reference design for 200-480VAC
May 11, 2022 · Features Three-phase inverter power stage suited for 200-480 VAC powered drives with output current rating up to 14 Arms Reinforced isolated gate driver with opto

Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · The output frequency of a high-frequency inverter is much higher than the power frequency, usually between a few kilohertz and ten kilohertz. With the use of high-frequency

6 FAQs about [Inverter output frequency and power]
What is a frequency inverter?
The frequency inverter is a power control equipment that applies frequency conversion technology and microelectronics technology to control AC motors by changing the frequency of the motor power supply.
What is the output current of an inverter?
It is important to understand that the inverter output current is determined by its power rating and the voltage supplied to the load. An inverter will only supply a continuous output current of I = P/V.
What is a PWM in a frequency inverter?
PWM: A frequency inverter control scheme in which a constant dc voltage is used to reconstruct a pseudo ac voltage waveform using a set of six power switches, usually IGBTs. Varying the width of the fixed-amplitude pulses controls effective voltage.
How does inverter speed regulation work?
Inverter speed regulation is achieved by changing the frequency of the power supply to the stator winding of the motor. First, the rectifier section converts the AC power supply to DC power. This usually involves a rectifier bridge, which converts the AC voltage to DC voltage.
How does a power inverter work?
When operating grid interactive, if the grid is available, the inverter can receive power from the grid or supply power to the grid. A power inverter controls voltage and current between the source (PV array, wind turbine, or other types of DC source) and the electrical loads and converts variable DC output into a quality sinusoidal waveform.
How do you connect a motor to a frequency inverter?
Connecting a motor to a frequency inverter is a straightforward process. Typically, the inverter is wired to the motor using three main power lines—one for each phase of the motor. In addition to the power connections, inverters often have terminals for switch inputs, which control the motor’s start/stop functions and direction of rotation.
Learn More
- The difference between inverter and high frequency power generation
- Power frequency inverter off-grid
- 5kva high frequency power inverter
- Seoul power frequency isolation 50kw inverter
- Dual voltage power frequency inverter
- New generation of intelligent industrial frequency high power inverter
- High power industrial frequency inverter
- Inverter power frequency high frequency
- Power inverter three-phase output
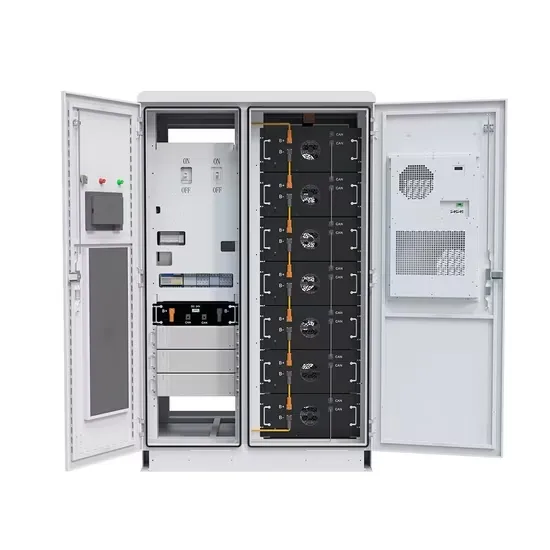
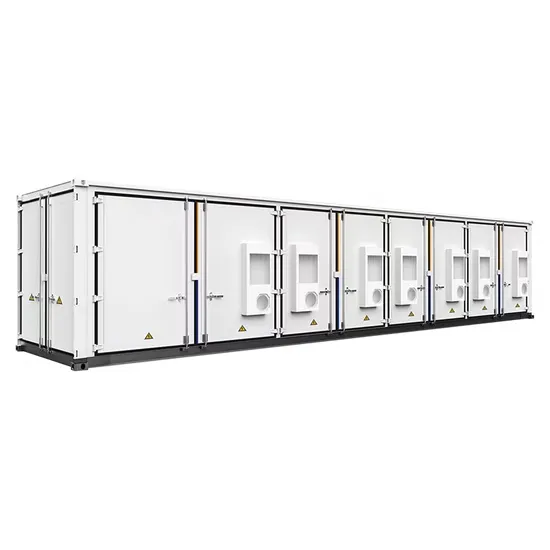
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
