
Power calculation and constant-power control
Jan 15, 2025 · The type of power measurement and control needs to be understood and properly applied for each application, i.e, whether motor shaft power, input inverter power or output

Design of a class E inverter with stabilized output power
1 day ago · Then, a system is developed that includes the inverter, converter, and PID controller to maintain constant output power, independent of the load.

A Family of Class EF Resonant Inverters With Constant AC Voltage Output
Jan 7, 2025 · Constant ac voltage output and zero-voltage switching can be achieved by the proposed inverter for a wide load range. To validate the theoretical analysis, the 1-MHz

Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What
3 days ago · The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input source into alternating current

Inverter Generator Basics: Classification and
Jun 21, 2024 · An inverter generator is a device that can control the output power and speed of a generator by adjusting the frequency. It can output constant

Multi-Functional PV Inverter With Low Voltage Ride-Through and Constant
Mar 11, 2022 · Unlike other PV inverters, the controller maintains the maximum-power-point-tracking (MPPT) in all conditions. LVRT, constant power output, and robust MPPT are the

Output Power and Power Factor : Solis North
Jun 15, 2022 · Output Power Within the Advanced Settings menu is a submenu called "Power Control". In this menu there are two settings that can

Constant-Current-Output and High-Efficiency Class E Inverter
Aug 30, 2024 · Constant-Current-Output and High-Efficiency Class E Inverter with Wide-Range Load Published in: 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration

Setting Reactive Power Control
The Q-U hysteresis curve (CEI0-16) control mode is the Italian standard CEI0-16 version of the Q-U characteristic curve. It dynamically adjusts the output reactive power of the inverter or Smart

Power Factor and Grid-Connected Photovoltaics
Nov 23, 2020 · Power Factor and Grid-Connected Photovoltaics As the level of Grid-Connected PV penetration continues to rise, the importance of power factor and power factor correction is

Power calculation and constant-power control
Jan 15, 2025 · When the motor output power is constant, the motor speed reflects the air/flow resistance. One solution is to control the cubic volume of air flow by the closed loop based on

REGULATING VOLTAGE: RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
Jan 12, 2025 · The new smart inverters are designed to allow customer-sited generation to act more in concert with the existing grid, with key features making these devices more grid

Design of constant output voltage DC-AC inverter for
In batteryless solar PV, the output voltage of solar PV always varies according to solar irradiation, temperature, so that it becomes a challenge in modelling DC-AC inverter with constant output

A strategy of PI + repetitive control for LCL-type photovoltaic inverters
Apr 8, 2020 · Due to the traditional grid-connected current control method of single Proportional Integral (PI) and Repetitive Control (RC) strategies, the photovoltaic inverter output current will
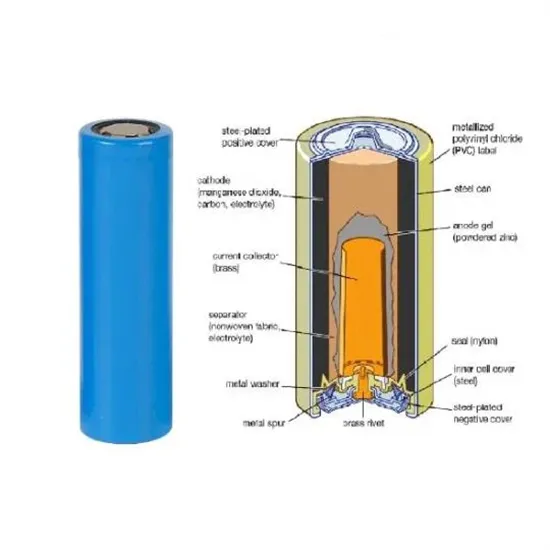
What Is A Constant Power Inverter?
Aug 14, 2024 · Its primary function is to ensure consistent output power to meet the electrical needs of various loads. Unlike traditional inverters, Constant Power Inverters offer higher

Design of constant output voltage DC-AC inverter for
The output of DC-AC inverter connected to constant specific loads that are only required during the day to solve the problem of power availability in deserts, farm, forest, and for the working

Constant-Current-Output and High-Efficiency Class E Inverter
Aug 30, 2024 · wireless charging always suffers efficiency degradation from load variation, which seriously constrains its wide application. In this research, a T-match network is introduced in

A Detuning-Repeater-Based Dynamic Wireless Charging
Sep 5, 2022 · High-density coil installation to achieve a smooth power transfer inevitably increases construction costs, reducing the acceptance of dynamic wireless power transfer

How to Design a Simple Constant Current/Constant
Apr 1, 2023 · ABSTRACT Technical Information about designing a constant current, constant voltage (CC/CV) power converter is limited. The design implementation can be challenging

6 FAQs about [Inverter output constant power]
How does an inverter work?
The inverter first converts the input AC power to DC power and again creates AC power from the converted DC power using PWM control. The inverter outputs a pulsed voltage, and the pulses are smoothed by the motor coil so that a sine wave current flows to the motor to control the speed and torque of the motor.
How does an inverter control a motor?
An inverter uses this feature to freely control the speed and torque of a motor. This type of control, in which the frequency and voltage are freely set, is called pulse width modulation, or PWM. The inverter first converts the input AC power to DC power and again creates AC power from the converted DC power using PWM control.
What are the output F/V characteristics of an inverter?
The output F/V characteristics of the inverter, that is, the load torque output mode, are basically divided into two types: a constant relationship (corresponding to constant torque mode) and an exponential relationship (corresponding to the fan-type load mode), not divided into constant power and constant torque.
How does an inverter affect the speed of an AC motor?
The use of an inverter to adjust the speed and acceleration of an AC motor increases the range of applications of the motor compared with a motor that operates at a constant speed. The speed of a motor is normally measured as the number of revolutions per minute (rpm).
How does a general-purpose inverter work?
The pulses are smoothed by the motor coil, and a sine wave current flows. As a result, the output from a general-purpose inverter cannot be used for equipment other than motors. V/f control is a method of controlling a motor by supplying a specific current to the coil to output a specific torque.
How to select an inverter based on motor capacity selection?
Select an inverter that can be used with the motor you selected based on the result of motor capacity selection. Basically, select an inverter which fits the maximum applicable motor capacity of the selected motor. After selecting an inverter, check if it meets the both of the following conditions.
Learn More
- Inverter output frequency and power
- Power inverter three-phase output
- Inverter increases power output
- 24V4000W inverter output power
- Single-phase inverter output power design
- Indonesian wind power off-grid inverter
- Congo low power inverter price
- Is the output of the inverter DC
- What is the maximum power of a 12v high power inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
