
Review of control techniques for inverters parallel operation
Dec 1, 2010 · Next, the different techniques to parallel inverters suggested in the literature will be checked. These can be categorized to the following main approaches: master/slave control

Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters | EEEGUIDE
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters: It has already been mentioned that Inverter Control providing a variable frequency supply to three phase motors should be capable of providing a

Comparison of Voltage Control by Inverters for Improving
Sep 2, 2020 · Voltage rise caused by reverse power flows and intermittency in renewable power is the main limiting factor for integration of photovoltaic (PV) generation in lo

CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
Mar 27, 2016 · An inverter uses this feature to freely control the speed and torque of a motor. This type of control, in which the frequency and voltage are freely set, is called pulse width

Voltage and Harmonic Control of Inverters
External filter circuits cannot be employed due to the difficulty in operating inverters over a wide range of frequencies. It is therefore necessary to keep down the harmonic content of the ac

Regulating Voltage: Recommendations for Smart Inverters
Mar 31, 2025 · This report from GridLab provides an introduction to voltage regulation concepts, including advantages and disadvantages of various control modes. The authors include

REGULATING VOLTAGE: RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
Jan 12, 2025 · reduce this voltage impact by absorbing reactive power. Smart inverters, which have the ability to more quickly control reactive power, can be better suited than traditional

How to enable Volt-Var / Q (U) function : Service
Aug 4, 2023 · Inverter will change the reactive output power based on the grid voltage. Q (U) and the voltage control point can be adjusted. Default values

How does an inverter help stabilize voltage
Dec 26, 2024 · Inverters are power electronic devices that convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). In certain applications, they can play a crucial

Direct AC voltage control for grid-forming inverters
Dec 18, 2019 · Grid-forming inverters usually use inner cascaded controllers to regulate output AC voltage and converter output current. However, at the power transmission system level where

Differentiating between plant level and inverter level voltage control
Apr 1, 2022 · This signifies a paradigm shift in the manner in which voltage control is implemented in many conventional large solar and wind farms wherein today, voltage control is usually

Current-Controlled Voltage Source Inverter
A general inverter model that represents the currently dominant technology of current-controlled voltage-source inverters is presented in this section. Since the fault current contribution of

JETIR Research Journal
Sep 12, 2023 · Abstract: Voltage source inverters (VSIs) are key components in numerous power electronic systems, enabling the efficient conversion of DC power to AC power with variable
How does an inverter control current?
Oct 26, 2021 · The two go hand-in-hand. If, on average, you''re providing slightly more current than the load sinks, the voltage will be increasing as you charge the output capacitance, since

Inverter Basics: Classification and Applications
Jan 3, 2021 · Inverter Basics: Resonant Inverters This is the class of inverters in which output voltage or current is passed though zero to minimize switching

Voltage Control Using Inverter Reactive Power
Dec 20, 2023 · In this post, we''ll look at four reactive power control modes that can be selected in modern smart inverters to control inverter reactive power

6 FAQs about [Inverter can control voltage]
How to control AC voltage in an inverter?
Basically, there are three techniques by which the voltage can be controlled in an inverter. They are, Internal control of Inverter. In this method of control, an ac voltage controller is connected at the output of the inverter to obtain the required (controlled) output ac voltage.
What is internal control of inverter?
Internal control of Inverter. In this method of control, an ac voltage controller is connected at the output of the inverter to obtain the required (controlled) output ac voltage. The block diagram representation of this method is shown in the below figure.
What is a voltage source inverter?
Voltage source inverters (VSIs) are commonly used in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to generate a regulated AC voltage at the output. Control design of such inverter is challenging because of the unknown nature of load that can be connected to the output of the inverter.
Why are inverters used in motor control applications?
When inverters are used to feed such ac loads, it is necessary that the inverters provide provision for voltage variations so as to supply the required voltage to ac loads. In motor control applications, inverters handle the control of circuit voltage along with frequency so that the saturation of motor magnetic circuits is avoided.
What is voltage control of inverter?
Voltage control of inverters is employed in order to compensate for changes in input dc voltage. Basically, there are three techniques by which the voltage can be controlled in an inverter. They are, Internal control of Inverter.
How do inverter circuits work?
In this, the inverter circuit is fed from a constant dc voltage source and a controlled ac voltage is obtained at the output terminals by turning ON and OFF the switching components in the inverter circuit. The main drawback of this method is that it requires very low turn-ON and turn-OFF time thyristors which are very expensive.
Learn More
- Inverter can control voltage
- How does the inverter control the voltage
- Inverter voltage space vector control
- Inverter AC voltage automatic control
- Democratic Republic of Congo low voltage inverter price
- Automatic Voltage Regulator and Inverter
- Pure inverter voltage 175v
- Communication 48V inverter bus voltage
- 12v inverter protection voltage change
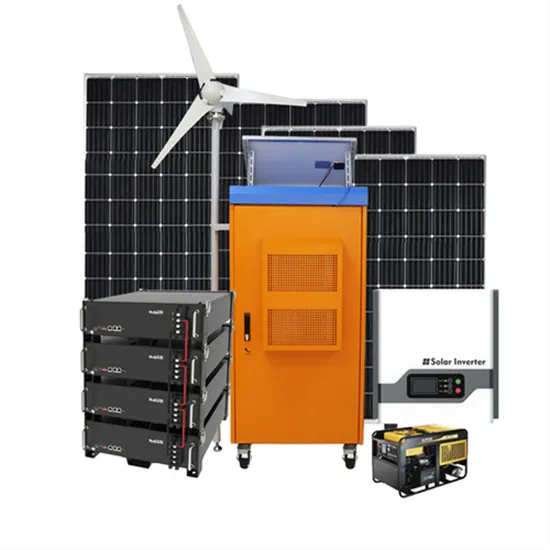
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
