
WHAT ARE THE DISADVANTAGES OF A HIGH FREQUENCY
FAQs about Advantages and disadvantages of DC high frequency inverter What are the advantages of high frequency inverters? High conversion efficiency: High operating frequency

Multilevel Inverters-A Comparative Analysis
Apr 25, 2017 · Input current: Multilevel inverters can draw input current with low distortion. frequency and high switching frequency PWM. It should be noted that lower switching

Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of power frequency
Apr 14, 2024 · With the rapid development of modern power electronics technology, inverters, as the key equipment for converting DC power into AC power, have been widely penetrated into

Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter- Which One Should I Prefer? To conclude, power-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters each have pros

HF (High frequency)
Apr 13, 2023 · In this article, we will explain what HF is, how it is used, and its advantages and disadvantages. Overview of High Frequency (HF) The high frequency band is the part of the

High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
Two main types of inverters are high-frequency and low-frequency inverters. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, making them more suitable for specific applications. Let''s
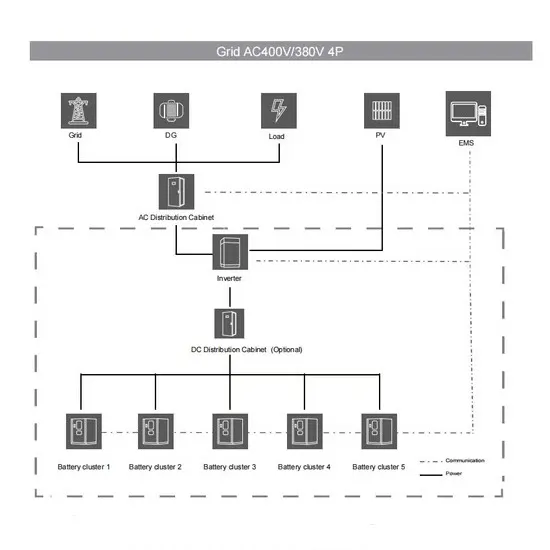
Advantages and disadvantages of multi-voltage high-frequency
Jun 12, 2025 · What are the advantages and disadvantages of multilevel inverters? Multilevel inverters nowadays are used for medium voltage and high power applications. The different

The Pros and Cons of Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Jul 30, 2014 · There are several types of sine wave inverters, of which true sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are the most popular models. Each of these sine wave

A technical review of modern traction inverter systems used
Nov 1, 2023 · These structures'' key characteristics, which make them ideal for the upcoming generation of traction inverters, include low-output current distortion, dv / dt reduction,

Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of power frequency
Apr 14, 2024 · High-frequency inverters, whose operating frequency significantly exceeds traditional power frequency inverters, specifically refer to a device that can convert low-voltage

Inverter and Types of Inverters with their
3 days ago · The two-level inverters have limitation in operating at high frequency in high voltage applications due to switching losses and constraints of the

Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key
Aug 15, 2025 · Explore the key differences in low frequency vs high frequency inverters including their applications, advantages, and which is best for your

Inverter Low Frequency vs High Frequency | How Do I
Mar 31, 2024 · Operating Frequency: High-frequency inverters are speed demons. They operate at a significantly higher frequency, often reaching 20,000 Hz or more. This high frequency

Inverter Low Frequency vs High Frequency | How Do I
Mar 31, 2024 · Advantages and Disadvantages of Inverter Low Frequency and High Frequency Now that we''ve got the fundamentals under our belt, let''s weigh the pros and cons. We''ll play

Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters:
Feb 10, 2025 · Smaller size and lighter weight: High-frequency inverters have the core advantage of using smaller and lighter internal electronic components

Low frequency inverter vs high frequency
Mar 12, 2025 · Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters: Compact & Lightweight: Easier to transport and install due to their smaller size. Higher Efficiency: More

6 FAQs about [What are the advantages and disadvantages of high frequency inverters]
What are the advantages of a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverters typically have an output of 20kHz or higher. Smaller size and weight compared to low-frequency inverters. Higher efficiency due to reduced power losses. Greater accuracy in output waveform due to the high frequency. Lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to higher switching frequency.
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
High-frequency inverters generally have higher efficiency than low-frequency inverters. This is because the higher operating frequency reduces the size of transformers, capacitors, and other components, leading to lower power losses. Low-frequency inverters have lower efficiency due to higher losses in magnetic components and switching devices.
What are the disadvantages of a low frequency inverter?
Some drawbacks of low frequency inverters include: Large Size Slower Response Distortion Acoustic Noise Lower Efficiency Some limitations of high frequency inverters: Complexity EMI Issues Reliability Concerns Acoustic Noise Higher Cost Low frequency inverters are advantageous for: High frequency inverters are better for:
What are the advantages of a low frequency inverter?
Simplicity, ruggedness, low EMI, and low acoustic noise are some of the advantages of low frequency inverters. They also have higher overload capacity. What semiconductor devices are commonly used in high frequency inverters?
Are high-frequency inverters a good choice?
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high efficiency, but they also have the problem of relatively poor output waveform quality.
Why are frequency drive inverters more efficient?
Efficiency and energy consumption: Because frequency drive inverters use high-frequency switching technology, their switching losses and iron losses are relatively small, so their efficiency is usually higher than that of power frequency inverters.
Learn More
- What is a high frequency inverter
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Micro Inverters
- Advantages and disadvantages of energy storage high power station
- Inverter power frequency high frequency
- Power frequency solar off-grid inverter high power
- Industrial frequency high frequency low frequency inverter
- High frequency sine inverter
- What are the ratios of photovoltaic inverters
- What are the inverters for household appliances
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
