
Power Inverters Explained: What They Are, How They Work,
May 21, 2025 · Run household appliances off-grid Convert solar energy into usable AC Support mobile and emergency setups 🔍 Types of Power Inverters 1. Pure Sine Wave Inverters Ideal for

What Is An Inverter? | Definition, Types, Uses,
Jan 25, 2025 · An inverter is a vital electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is used to power many household

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Inverter for Home
Oct 31, 2024 · Modified sine wave inverters Modified sine wave inverters are a relatively economical choice for most household appliances. This type of inverter is relatively
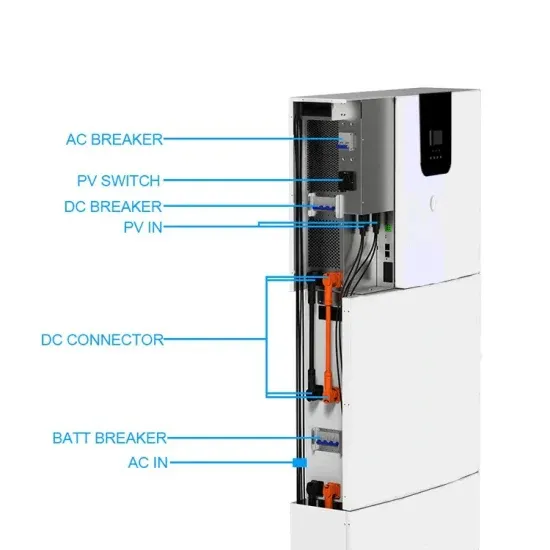
How Inverters Work with Batteries: A Beginner''s
Mar 4, 2025 · Inverters convert energy: The inverter takes the DC electricity from the batteries and converts it into AC electricity. Most household appliances
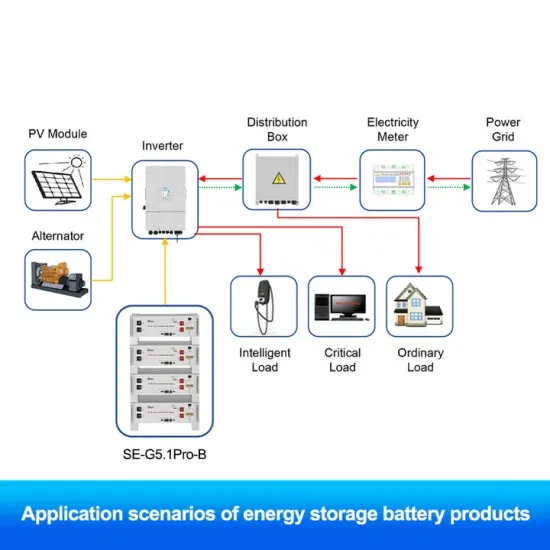
Inverters Explained: Function and Benefits | Lenovo IN
It is commonly used to power household appliances and electronic devices that require AC power when only DC power sources are available, such as in solar power systems or car batteries.

What Is an Inverter for Solar Panels and Why
Mar 28, 2025 · Solar inverters come in different types, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimisers, each offering unique benefits. Inverters

What Is a Power Inverter for Home Use? A Comprehensive
Jan 25, 2025 · A power inverter for home converts the DC power from a battery into usable AC power for your household appliances. By choosing the right size, wave type, and installation

What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Jul 8, 2025 · Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and

Choosing the Right Home Inverter: The Ultimate Guide
Feb 27, 2025 · This is important because most home electrical systems and appliances need AC power to work. Types of Home Inverters There are different types of inverters for homes, like

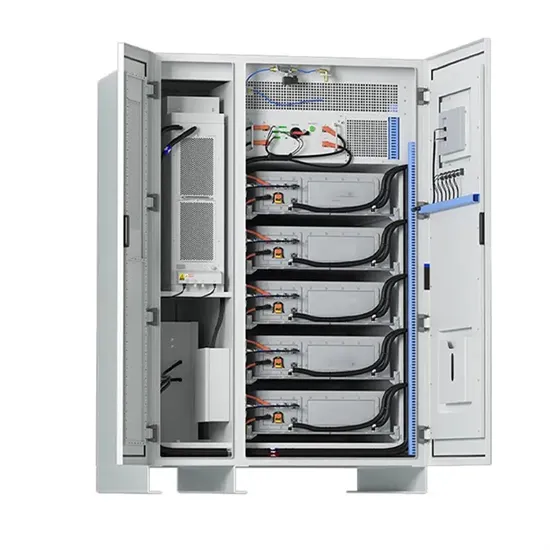
What Is An Inverter? | Definition, Types, Uses,
Jan 25, 2025 · Learn all about inverters—what they are, how they work, the types of inverters, and their applications. Discover the key components of inverters,

Inverters 101: What is an Inverter and How do
Mar 15, 2022 · In the simplest terms, an inverter is a device that regulates the frequency of electrical current coming into the appliance. This allows them to

Mastering Household Inverters: A Complete
Sep 7, 2023 · Welcome to our comprehensive guide on household inverters, your key to powering your home efficiently. In this article, we''ll unravel the mysteries of

6 FAQs about [What are the inverters for household appliances ]
What is a DC inverter?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working Principle: Inverters use power electronics switches to mimic the AC current’s changing direction, providing stable AC output from a DC source.
What is an inverter & how does it work?
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Think of it as a translator between two different electrical languages – your solar panels, batteries, and car electrical systems speak “DC,” while your home appliances, power grid, and most electronics speak “AC.”
Do inverters work with batteries?
Yes, inverters are commonly used with batteries in backup power systems, renewable energy setups, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). The inverter draws direct current (DC) power stored in the battery and converts it into alternating current (AC) to power appliances and devices.
What are inverters used for?
Inverters are essential components in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and whole-house backup systems. They provide seamless power during outages by converting stored battery power to AC electricity. Critical applications include:
Is an inverter a generator or a converter?
An inverter is a static device that converts one form of electrical power into another but cannot generate electrical power. This makes it a converter, not a generator. It can be used as a standalone device such as solar power or back power for home appliances.
What are the different types of inverters?
There are three main inverter types: sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave. Each kind fits different devices and specific uses. How do I choose the right inverter for my needs? Choose an inverter by your power needs and budget. Consider what devices you’ll power.
Learn More
- Inverters for household appliances
- What are the ratios of photovoltaic inverters
- What are the 196kw inverters
- Wholesale household inverters in Manila
- Choice of inverter for household appliances
- Does the solar power generation system use household appliances
- Hot sale wholesale household inverters Factory
- Wholesale household inverters in Bahrain
- What is the difference between sine wave inverters
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
