
The Impact of Variable DC-Bus Voltage Control on the Inverter
Jul 18, 2020 · The reliability of the power converters in electric vehicle applications has been a great concern. As most power converters are not designed with redundancy, a malfunction of

9. Inverter Settings
Sep 17, 2024 · 4. To set the voltage at which the inverter restarts after low voltage shut-down. - To prevent rapid fluctuation between shut-down and start up, it is recommended that this value

Inverter Voltage Calculator, Formula, Inverter Voltage
3 days ago · Inverter Voltage Formula: Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes

What Is Inverter Voltage?
Understanding inverter voltage —both input and output—is key to selecting the right inverter for your system. This guide explains the different types of inverter voltages and how to choose the

Interpreting inverter datasheet and main parameters | AE 868
Inverter and MPPT Depending on the topology, most modern inverters have built-in MPP trackers to insure maximum power is extracted from the PV array. Each inverter comes with a voltage
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What
3 days ago · Here are some important specifications that you need to know about input power inverters. Input Voltage: The input voltage supplied from the DC

Voltage Troubles? A Guide to Diagnosing Inverter Low Voltage
Dec 17, 2023 · Properly grounding your inverter is crucial to avoid voltage fluctuations. In conclusion, inverter low voltage problems are not uncommon, but with the right knowledge and

Photonik | String Voltage Calculator
Oct 13, 2023 · Solar String Voltage Calculator Why is calculating the string voltage so important? When designing a solar system using string solar inverters or solar charge controllers,

Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
Mar 31, 2010 · threshold: Point where voltage transfer curve intersects line Vout=Vin Represents the point at which the inverter switches state Normally, V ≈ Vdd/2 Sometimes other thresholds

Inverter Battery Voltage: How Many Volts Are Needed For
Mar 27, 2025 · An inverter battery typically operates at 12V, 24V, or 48V. These voltages represent the nominal direct current (DC) needed for the inverter''s function. Selecting the

REGULATING VOLTAGE: RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
Jan 12, 2025 · The new smart inverters are designed to allow customer-sited generation to act more in concert with the existing grid, with key features making these devices more grid

Inverter Protection and Ride-Through : RNWBL
Sep 22, 2022 · The inverter voltage control characteristic can be combined with a plant controller to provide Point of Interconnection (POI) voltage controls that

Lecture 23: Three-Phase Inverters
Feb 24, 2025 · However, most 3-phase loads are connected in wye or delta, placing constraints on the instantaneous voltages that can be applied to each branch of the load. For the wye

Understanding inverter startup voltage.
Jun 4, 2021 · Meaning that each individual string has to be of a certain size to reach the inverter start up voltage separately. For example; inverter start up voltage 90v. So each string has to

High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
May 14, 2025 · Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar
6 FAQs about [Voltage on the inverter]
What is inverter voltage?
Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC).
What voltage is a 12V inverter?
Inverters come in various configurations, each designed for specific power systems. Common rated input voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V. The choice depends on the application, the size of the power system, and the available power source. A 12V inverter is commonly used for smaller applications, such as in vehicles or small off-grid setups.
What is an example of a power inverter?
Common examples are refrigerators, air-conditioning units, and pumps. AC output voltage This value indicates to which utility voltages the inverter can connect. For inverters designed for residential use, the output voltage is 120 V or 240 V at 60 Hz for North America. It is 230 V at 50 Hz for many other countries.
What is a start inverter voltage?
The start inverter voltage is the minimum input voltage required for the inverter to initiate the conversion process. In the case of a 12V inverter, the start inverter voltage is typically around 9.5VDC. This threshold ensures that the inverter can begin its operation reliably without placing undue stress on the connected battery.
How do you calculate inverter voltage?
Understanding and calculating inverter voltage is crucial for ensuring the correct operation and efficiency of various electronic devices and systems. Inverter voltage, V (V) in volts equals the product of DC voltage, V DC (V) in volts and modulation index, dm. Inverter voltage, V (V) = V DC (V) * dm V (V) = inverter voltage in volts, V.
How much power does an inverter need?
It’s important to note what this means: In order for an inverter to put out the rated amount of power, it will need to have a power input that exceeds the output. For example, an inverter with a rated output power of 5,000 W and a peak efficiency of 95% requires an input power of 5,263 W to operate at full power.
Learn More
- Inverter string output voltage
- Can the DC 12V voltage be supplied to the inverter
- Argentina voltage stabilizer inverter manufacturer
- Inverter voltage modulation
- 350w inverter voltage to 220v
- 12v inverter high voltage
- 27V inverter input voltage
- The higher the voltage the higher the high frequency inverter
- The difference between high voltage and low voltage inverter
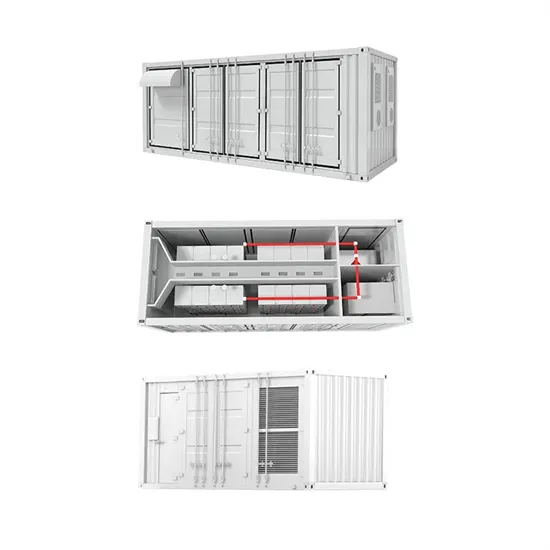
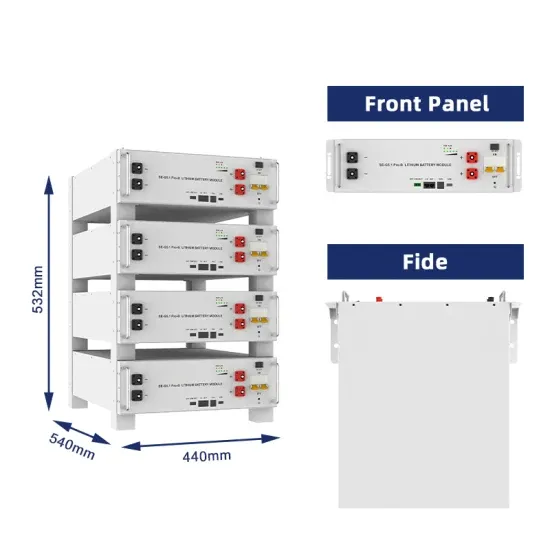
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
