
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
3 days ago · Learn about different types of inverters that convert DC into AC, such as voltage source inverter, current source inverter, single phase inverter, three phase inverter, and more.

Inverter Basics: Classification and Applications
Jan 3, 2021 · Inverter Basics: Resonant Inverters This is the class of inverters in which output voltage or current is passed though zero to minimize switching

High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
May 14, 2025 · Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar

What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Jul 8, 2025 · Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
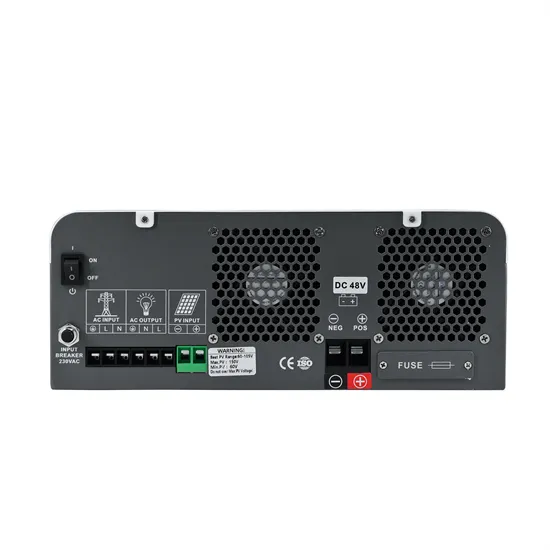

Low Voltage Inverter: Definition, Function, And Applications
3 days ago · This article will discuss the definition, function, and applications of low voltage inverters, especially in renewable energy systems such as solar power.
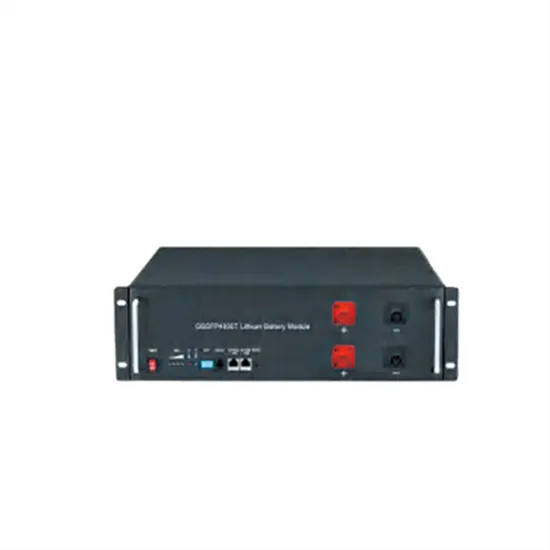

Infineon high voltage Inverter Application Presentation
May 25, 2025 · Infineon high voltage Inverter Application Presentation Traction Inverter trends Semiconductors contribute to improved energy efficiency, but also to size and weight

什么是逆变器,变频器?它是如何工作的?
Jul 6, 2023 · 逆变器由三个元件组成:将交流电流转换为直流电流的 转换器电路 、 电容器 和 功率逆变器电路。 首先,转换器电路将交流电转换为直流电,

High Voltage Solar Inverter DC-AC Kit
Sep 3, 2014 · High Voltage Solar Inverter DC-AC Kit 1 Introduction Inverters, especially solar inverters, have gained more attention in recent years. Solar inverters produce solar energy

Regulated Inverting Charge Pumps | Analog Devices
Analog Devices'' family of regulated inverting charge pumps are used to invert an input voltage to a regulated output voltage. These are useful for systems with split-rail positive and negative

Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition,
Dec 16, 2024 · Inverter voltage is a voltage generated by the inverter after several electrons that converts a series of direct current (DC) into alternating current
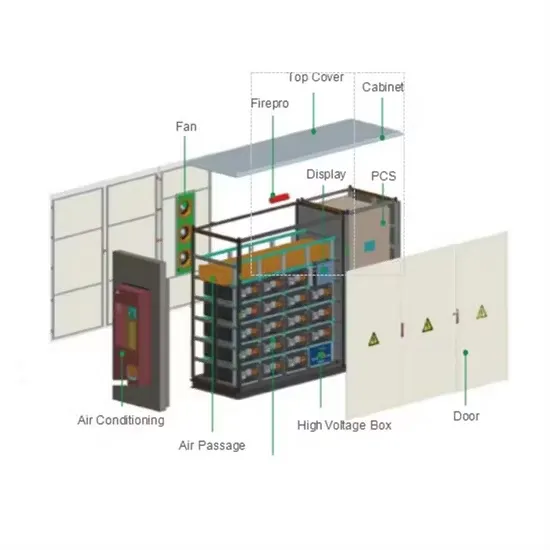
High Voltage Inverters & Batteries | Solar Warehouse SA
What is a High Voltage Inverter? A high voltage inverter is a device that converts the direct current (DC) electricity from solar panels or batteries into high voltage alternating current (AC)

Introduction to multilevel voltage source inverters
Jan 1, 2021 · Multilevel inverters (MLIs) are improved alternative devices to regular two-level inverters, to decrease dv/dt and di/dt ratios while providing an increased number of output

Vertiv MegaVert-G系列中压变频器
Vertiv™ MegaVert™系列中压变频器,承载着超过14年的深厚研发历史和创新精神。自2009年由原艾默生网络能源有限公司(Emerson Network Power Ltd.)推出,便凭借高可靠性能大受市场

6 FAQs about [Voltage inverter]
What is a power inverter?
Unlike rectifiers which convert AC into DC; Inverter is a type of converter that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) of desired voltage and frequency with the help of control signals and electronic switches. Here in this post, we are going to discuss inverter basics, classification and application of power inverters.
What is a voltage source inverter?
The inverter is known as voltage source inverter when the input of the inverter is a constant DC voltage source. The input to the voltage source inverter has a stiff DC voltage source. Stiff DC voltage source means that the impedance of DC voltage source is zero. Practically, DC sources have some negligible impedance.
What is a DC inverter?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working Principle: Inverters use power electronics switches to mimic the AC current’s changing direction, providing stable AC output from a DC source.
What is a voltage inverter circuit?
The voltage inverter circuit is shown below, that uses a well known LM555IC timer chip. The schematic diagram divided into three parts, namely an oscillator, rectifier, and voltage regulator.An oscillator is used to convert DC into AC, a special type of rectifier is used to convert AC to DC and finally a voltage regulator.
What are the different types of voltage inverters?
Inverters are used in a large number of electrical power applications. Voltage inverters are divided into three categories, Pulse-width Modulated Inverters, Square-wave Inverters, and Single-phase Inverters with Voltage Cancellation. Voltage Inverter Working Principle?
What is the difference between an inverter and a converter?
An inverter is an electrical device, which converts DC power to AC power and either increases or decreases the voltage level accordingly. In comparison, a converter changes the voltage level but does not change its type. So in converters, an AC voltage would still be AC and a DC voltage would still be in DC.
Learn More
- Inverter string output voltage
- Can the DC 12V voltage be supplied to the inverter
- Are there any requirements for the high voltage at the back end of the inverter
- Inverter increases peak voltage
- Inverter adjusts voltage to 220
- 12v inverter high voltage
- 27V inverter input voltage
- The higher the voltage the higher the high frequency inverter
- Voltage inverter b9zz560151
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
