
Working principle and function of frequency converter
Aug 28, 2024 · The inverter adjusts the voltage and frequency of the output power supply by the internal IGBT disconnection, and provides the necessary power supply voltage according to

How to Choose the Right Frequency Inverter for Your
Jul 30, 2025 · Select the right frequency inverter in 2025 by matching motor specs, load type, control method, and environment for reliable, efficient performance.

Introduction to the Frequency Converter Working Principle
Jul 17, 2024 · Control circuit: Receives feedback signals from the motor and the grid, periodically controls the switching devices of the inverter to adjust the output voltage and frequency, and

Working Principle of an Inverter
Dec 3, 2024 · Inverters often incorporate a voltage regulation system to ensure the AC output matches the required voltage and frequency for specific applications. For example, most
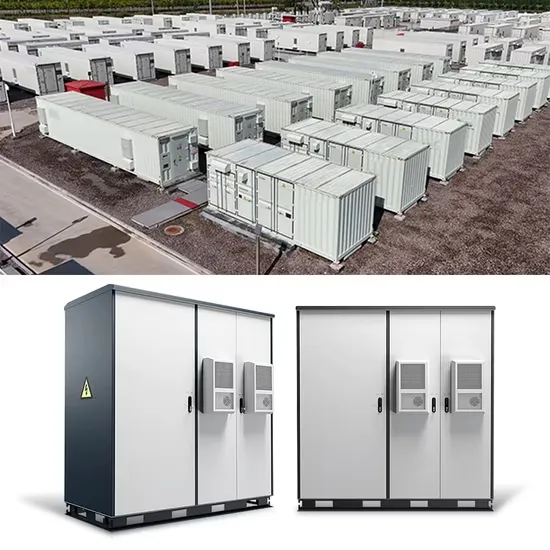

Guide to Frequency Inverters: Optimizing Motor
Nov 13, 2024 · Inverter programming should include adjustments for parameters such as speed control, voltage-to-frequency ratio, and torque characteristics,

The difference between variable frequency starting and industrial
Frequency conversion starting: Frequency conversion starting is a motor starting method that controls the motor speed by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the AC power through the

Understanding Frequency Inverters: A Comprehensive Guide
Feb 23, 2025 · A frequency inverter, also known as a variable frequency drive (VFD), is an essential device used to control the speed and torque of electric motors by adjusting the input

Emerging Trends in Frequency Inverters for Industrial
A frequency inverter is a device that controls the speed and torque of electric motors by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to them. It plays a crucial role in industrial

Key Differences Between Frequency Inverters and Inverters
Dec 3, 2024 · A frequency inverter adjusts the frequency and voltage of AC power to control motor speed, making it ideal for industrial applications like manufacturing and HVAC systems.

AC Motor Inverters: How They Work, Principles, And
May 19, 2025 · This process allows the inverter to control the motor''s speed and efficiency effectively. AC motor inverters utilize pulse width modulation (PWM) to create a variable

Motor Inverter vs VFD: What''s the Real Difference? | Mingch
Aug 4, 2025 · A motor inverter and a variable frequency drive (VFD) are related, but not identical. The term motor inverter often refers to the DC-to-AC conversion stage that powers a motor. At

What Are the Differences Between Voltage Converters and
Jan 31, 2025 · Linear Voltage Regulators: These adjust the working state of electronic components to linearly step down the input voltage to the target level, offering stable output

How Industrial Inverters Help Reduce Energy Costs in Factories
May 24, 2025 · An industrial inverter, often referred to as a variable frequency drive (VFD) or frequency inverter, is a device that adjusts the speed and torque of electric motors by varying
Key Differences Between Frequency Inverters and Inverters
A frequency inverter adjusts the frequency and voltage of AC power to control motor speed, making it ideal for industrial applications like manufacturing and HVAC systems.

Principle and application of frequency converter
Aug 21, 2024 · The inverter adjusts the voltage and frequency of the output power supply by changing the internal power switch (such as IGBT) to adjust the voltage and

How Does An Inverter Convert DC To AC? | The
Jan 25, 2025 · The inverter adjusts the voltage and frequency to match that of standard grid electricity, ensuring appliances function properly. For appliances

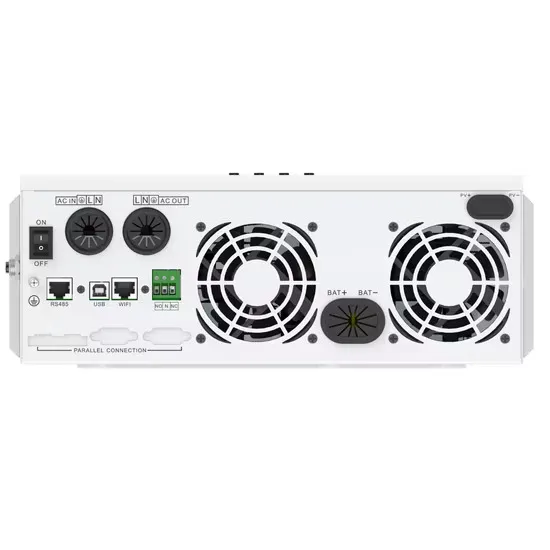
6 FAQs about [Industrial frequency inverter adjusts the working voltage]
How does a frequency inverter work?
Frequency inverter relies on the internal IGBT to adjust the voltage and frequency of the output power supply, according to the actual needs of the motor to provide the required power supply voltage, and then achieve the purpose of energy saving and speed regulation.
What is frequency control in inverter?
Frequency Control: The frequency of the output AC voltage is determined by the switching frequency of the IGBTs in the inverter stage. For instance, if an electric motor is designed to operate at a synchronous speed of , where is the speed, is the frequency of the power supply, and is the number of poles of the motor.
What is the basic design of a frequency inverter?
The basic design of a frequency inverter consists of just electronic components, without any mechanically moving components. Frequency inverters are made up of the following main assemblies: The rectifier converts the AC voltage on the input side into DC voltage.
How does inverter speed regulation work?
Inverter speed regulation is achieved by changing the frequency of the power supply to the stator winding of the motor. First, the rectifier section converts the AC power supply to DC power. This usually involves a rectifier bridge, which converts the AC voltage to DC voltage.
Why are frequency inverters important?
In conclusion, frequency inverters are sophisticated yet essential devices that have revolutionized the way electrical equipment, especially motors, are controlled. Their ability to adjust frequency and voltage precisely has led to significant improvements in energy efficiency, performance, and flexibility in numerous applications.
How do frequency inverters affect motor performance?
A frequency inverter’s primary function is to manage motor performance by adjusting the electrical supply, but the way it does this can vary depending on the method of control used and the motor's specific demands. Here's a breakdown of how frequency inverters influence motor performance:
Learn More
- Three-phase industrial frequency inverter wholesale price
- Ghana industrial frequency off-grid inverter price
- Algeria industrial frequency pure sine wave inverter
- New generation of intelligent industrial frequency high power inverter
- What is the best voltage for a power frequency inverter
- Riyadh single phase 110v industrial frequency inverter
- Abuja Industrial Frequency Pure Sine Wave Inverter
- The higher the voltage the higher the high frequency inverter
- Assembly of high power industrial frequency inverter
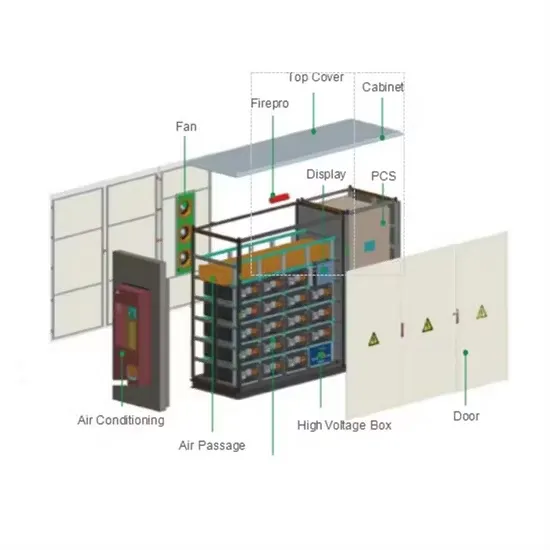
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
