
Bucharest Rail Maps and Stations from European
Introduction Like many of Europe''s the most influential cities, Bucharest is located on the banks of a river, in this case the River Dâmboviţa. As well as the river,

Teltronic Cuts TETRA Base Station Power Use by 70%
Jun 19, 2025 · In a significant technological stride, Teltronic, the Spanish telecommunications leader with more than five decades of experience in mission-critical communications, has
Green Communications | Engineering And Technology Journal
The main goal of designing green base stations is to save energy and reduce power consumption while guaranteeing user service and coverage and ensuring the base station''s capability for

Green City Action Plan for the Municipality of Bucharest
Nov 15, 2023 · Furthermore, the representation of the European Commission in Romania is a communication gateway between the municipality of Bucharest and the Commission

GBS, new TETRA base station with AI to reduce consumption
Jun 18, 2025 · Teltronic, a Spanish company with 50 years of experience in the design, development, and deployment of critical communications solutions, has introduced its new

Teltronic Introduces New Green Communications Base Station
Jun 19, 2025 · Spain''s Teltronic has introduced its new GBS (Green Base Station) during the Critical Communications World event. This next-generation TETRA base station integrates

Salary: Communications Coordinator in Bucharest, Romania
Jun 20, 2023 · The estimated salary for a Communications Coordinator is RON 4,521 per month in the Bucharest Romania area. This number represents the median, which is the midpoint of

Green Bucharest: local businesses that champion sustainability
In a city where green space per resident is under 10 m², according to the Romanian Centre for European Policie s, sustainability is no longer a buzzword—it''s a necessity. Bucharest may

Communications Vice President Salary Bucharest, Romania
The average communications vice president salary in Bucharest, Romania is 283.051 RON or an equivalent hourly rate of 136 RON. Salary estimates based on salary survey data collected

Green Bucharest: local businesses that champion sustainability
In a city where green space per resident is under 10 m², according to the Romanian Centre for European Policies, sustainability is no longer a buzzword—it''s a necessity. Bucharest may

Green base station
Apr 13, 2008 · The four main elements of the solution are: minimizing the number of base station sites; minimising the need for air conditioning to cool the sites; using the latest base station

Step by step guide to public transport in Bucharest
Bucharest had some very nice improvements over the last few years in terms of public transport. Everything is now more reliable and brand new trams and busses took over the relatively old

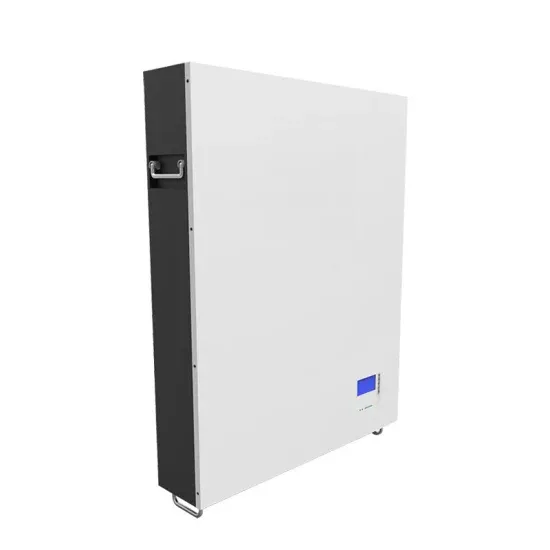
6 FAQs about [What brand is the green base station of Bucharest Communications ]
What is a green base station solution?
The green base station solution involves base station system architecture, base station form, power saving technologies, and application of green technologies. Using SDR-based architecture and distributed base stations is a different approach to traditional multiband multimode network construction.
Are green cellular base stations sustainable?
This study presents an overview of sustainable and green cellular base stations (BSs), which account for most of the energy consumed in cellular networks. We review the architecture of the BS and the power consumption model, and then summarize the trends in green cellular network research over the past decade.
Does Ericsson have a 'green' base station design?
But the large equipment vendors too have got in on the act. Ericsson made a point of its green credentials at the recent Mobile World Congress, and launched a "green" base station design back in 2007. Its commitment extends from materials used in base station build, to the design and efficiency of the base stations themselves.
What should a base station do in a wireless communications network?
In a wireless communications network, the base station should maintain high-quality coverage. It should also have the potential for upgrade or evolution. As network traffic increases, power consumption increases proportionally to the number of base stations. However, reducing the number of base stations may degrade network quality.
What is the difference between a traditional base station and SDR soft base station?
The biggest difference between a traditional base station and an SDR soft base station is that the Radio Frequency Unit (RU) of the soft base station is capable of software programming and redefining. So an SDR soft base station can intelligently allocate spectrum and support several standards.
What is a soft base station?
The modular design of an SDR soft base station allows innovation on the base station’s form. Two innovative forms are distributed base station and super baseband pool. In distributed base station, the Base Band Unit (BBU) is separated from the Remote Radio Unit (RRU), making network deployment more flexible.
Learn More
- Huawei Communications Green Base Station in Eritrea
- Kenya Communications Green Base Station Equipment
- Brussels Communications Green Base Station Installs Energy Storage
- Nuku alofa Communications Green Base Station Construction Unit
- New Zealand Communications Green Base Station Cabinet Manufacturer
- London Communications Green Base Station Equipment Processing Factory
- Huawei Communications Green Base Station in Lesotho
- New Delhi Communications Green Base Station Equipped with Equipment
- How much power does Phnom Penh Communication Green Base Station generate
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
