
Design and Implementation two three-phase inverters
Aug 24, 2024 · Abstract—In this work we studied, designed, and released two three-phase inverters fed dual-star induction machine (DSIM) prototype which is used in different areas. To

Two-level three-phase voltage source inverter
Dec 23, 2020 · Generally, a three-phase voltage source inverter generates eight switching states, including six active and two zero states, by the bipolar method. This study proposes a novel

What is a Three-Phase Inverter? | inverter
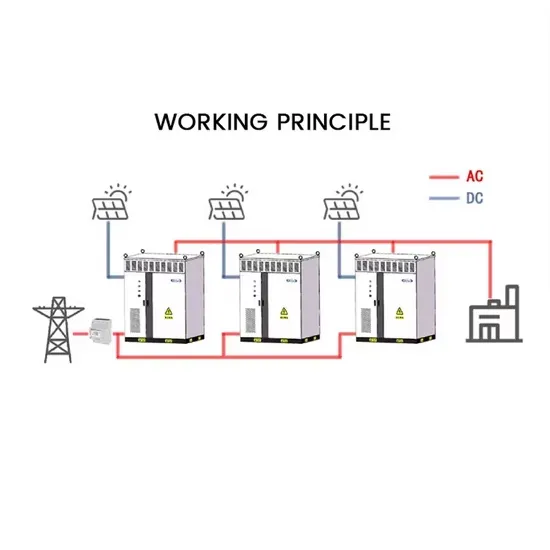
Sep 17, 2024 · Modular design is a key direction for future three-phase inverter design. By dividing inverters into multiple independent modular units, quick installation, maintenance, and

Lecture 23: Three-Phase Inverters
Feb 24, 2025 · Lecture 23 - 3-phase inverters Prof. David Perreault Consider implementation of an inverter for 3-phase using three single-phase inverters (e.g. full-bridge or half-bridge), one

Common Mode EMI Reduction through PWM Methods
Jun 25, 2019 · Abstract—Pulse-width sequences are identified as the determining factor for common-mode (CM) voltage, which together with CM path generate CM current. This paper

Topology and control method of double boost 3-level inverters
1 day ago · SC-inverters achieve boost through series and parallel combinations of SCs, without the need for additional boost equipment, reducing system costs and volume. The common

LOSS COMPARISON OF TWO AND THREE-LEVEL
Mar 13, 2024 · This paper examines the semiconductor and DC-link capacitor losses of four voltage source inverter topologies: the conventional two-level inverter, the two-level two

Comparative Evaluation of 800V DC-Link Three-Phase Two/Three
Nov 27, 2020 · The adoption of wide band-gap (WBG) semiconductors is gaining momentum, particularly in industries where high efficiency and/or extreme power density are major

A Multilevel Open-End Winding Six-Phase Induction Motor Drive Topology
Oct 14, 2021 · This paper presents a nine-leg (9L) multilevel inverter to drive a six-phase induction machine in an open-end winding (OEW) configuration. The system is based on three

Advanced Carrier-Based Pulse-Width Modulation of Three-Phase Two
Dec 27, 2024 · Many industrial applications require voltage control of inverters to maintain constant output voltage irrespective of variations in the input dc voltage and for constant

Improved control method of the paralleled three-phase two
Aug 1, 2024 · The three-phase two-level (3P2L) inverter has salient features of simple structure, superior output waveforms, and low system cost [1]. Thus, it has been extensively used in

Two‐Phase Inverters with Minimum Switching Devices
Jun 14, 2017 · Abstract The chapter deals with two-phase inverters with minimum switching devices whereby the main emphasis is devoted to ''minimum switches converter topologies
Two-stage three-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
Jun 1, 2025 · In this article, a novel control method of the grid-connected inverter (GCI) based on the off-policy integral reinforcement learning (IRL) method is presented to solve two-stage

Two Compact Three-Phase Multilevel Inverters for Low
Aug 31, 2022 · In this article, two compact three-phase multilevel inverters are proposed. The first proposed topology consists of three dc sources and ten power switches. The merit of the first

A Variable Switching Frequency Space Vector Modulation Technique
Oct 23, 2018 · A variable switching frequency space vector modulation control method is proposed in this paper. It is used to achieve zero-voltage switching (ZVS) for two parallel 180°

Improved control method of the paralleled three-phase two
Aug 1, 2024 · Abstract The paralleled configuration of three-phase two-level (3P2L) inverters has been put forward to increase the output power rating, operating efficiency, and system reliability.

6 FAQs about [Two three-phase inverters]
What are two-level and three-level inverters?
Two-level and three-level inverters are types of power electronic systems designed to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). They are commonly used in various applications such as UPS, electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and motor drives. Here are the key differences between these two types of inverters: Voltage Levels
What is 3p2l inverter?
Introduction The three-phase two-level (3P2L) inverter has salient features of simple structure, superior output waveforms, and low system cost . Thus, it has been extensively used in varieties of industry applications, such as renewable energy system, ac motor drive system, power quality control, etc.
How does a 3 phase inverter work?
However, most 3-phase loads are connected in wye or delta, placing constraints on the instantaneous voltages that can be applied to each branch of the load. For the wye connection, all the “negative” terminals of the inverter outputs are tied together, and for the detla connection, the inverter output terminals are cascaded in a ring.
What are the problems of a three-phase inverter?
Another issue of the three-phase inverter is the common-mode voltage (CMV), which is excited by the switching behavior of the power semiconductor devices .
What are the different types of inverters?
They are commonly used in various applications such as UPS, electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and motor drives. Here are the key differences between these two types of inverters: Voltage Levels Two-Level Inverter: This type of inverter has two voltage levels at the output.
How is a three-phase PV Grid-connected inverter designed?
The three-phase PV grid-connected inverter was designed based on the LQR method, where the tracking error was adjusted to zero through integration (Al-Abri et al., 2024). The disturbance rejection ability of the PV GCI was improved by designing the linear state inaccuracy feedback control policy (Zhou et al., 2021).
Learn More
- How to choose capacitors for three-phase inverters
- Differences between single-phase and three-phase inverters
- How many inverters are there for communication base stations in West Africa
- On Photovoltaic Inverters
- Disadvantages of Solar Inverters
- Selling solar inverters in Porto Portugal
- There are many inverters in Western European communication base stations
- Hot sale factory price 3000w inverters company
- Multiple photovoltaic panels connected to inverters
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
