
What is 5G base station architecture?
Dec 1, 2021 · The higher the frequency, the more data it transmits. 5G core network architecture operates on different frequency bands, but it''s the higher frequencies that deliver the most

Communication Base Station Testing Standards | HuiJue
The Invisible Guardians of 5G Connectivity As global 5G adoption surpasses 1.5 billion connections in 2024, communication base station testing standards have become the unsung

MCMC MTSFB TC T017_2021
Sep 1, 2021 · This Technical Code applies to IMT-2020 (Fifth Generation) Base Station (5G BS) based on the technologies as specified in applicable Malaysian Standards, technical codes,

Optical Communications in the 5G Era
Abstract In the opening chapter of this book, we first describe the 5G era in terms of the evolution of mobile networks from 1G to 5G, the main application scenarios of 5G, and the development

A Field Guide to 5G Standards in Satcom/Telecom Integration
Jun 11, 2024 · Learn how innovations like 5G NTN and ORAN are driving the convergence of terrestrial and non-terrestrial communications. Explore the latest in regenerative payloads,

Chapter 2: Architecture — Private 5G: A Systems
Jul 3, 2025 · To further confuse matters, 3GPP terminology often changes with each generation (e.g., a base station is called eNB in 4G and gNB in 5G). We

A Secure Transmission Strategy for Smart Grid Communications
Dec 26, 2024 · As the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in smart grids grows, security issues arise, including eavesdropping. The fifth generation (5G) wireless technologies are the

Technical Requirements and Market Prospects of 5G Base Station
Jan 17, 2025 · With the rapid development of 5G communication technology, global telecom operators are actively advancing 5G network construction. As a core component supporting

Installation of Base Stations and Radiation Safety
Jul 21, 2025 · The rollout of 5G services needs the establishment of an extensive network of radio base stations and small cells to support very high-speed data transmission and ubiquitous
5G Base Station Deployment Review for RF Radiation
Oct 31, 2021 · This paper reviews the recent works on the Electromagnetic Fields (EMF) radiation assessment for 5G base stations (BS) on human evaluation and analysis from different

Research on the Impact of 5G Terminals on Electromagnetic
Mar 1, 2024 · The Ministry of Ecology and Environment released the "5G mobile communication base station electromagnetic radiation environmental monitoring methods (for trial

5G Network Architectures and Technologies
Aug 1, 2025 · Standalone (SA): standalone networking. SA uses an end-to-end 5G network architecture, where 5G standards are used on terminals, base stations, and core networks. SA

Optimize Signal Quality In 5G Private Network Base
Dec 8, 2023 · In conjunction with 5G NR, private base stations (BS) can support connectivity for different spectrum bands (sub-GHz, 1 to 6 GHz, or mmWave). The 5G base station products

Research on Electromagnetic Radiation Safety Assessment of
Oct 16, 2022 · Electromagnetic radiation safety of 5G base stations has been widely concerned by society and the public due to the accelerated development. This paper analyzes the

5G Mobile Communication Base Station Electromagnetic
Dec 15, 2023 · The current national policies and technical requirements related to electromagnetic radiation administration of mobile communication base stations in China are described,

Technical Requirements and Market Prospects of 5G Base Station
Jan 17, 2025 · As core components, 5G base station chips must meet the following key technical requirements: 1.High Spectrum Efficiency and Large Bandwidth Support. 5G networks use a

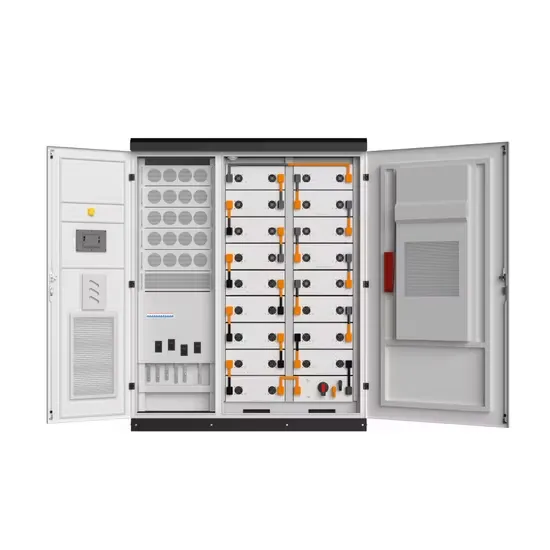
What Is 5G Base Station?
Apr 8, 2025 · Base stations, also called public mobile communication base stations, are interface devices for mobile devices to access the Internet. They are also a form of radio stations, which

6 FAQs about [Communication 5g base station standards]
What are the different types of 5G NR base stations?
This article describes the different classes or types of 5G NR Base Stations (BS), including BS Type 1-C, BS Type 1-H, BS Type 1-O, and BS Type 2-O. 5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB.
Are 5G base stations 3GPP compatible?
In conjunction with 5G NR, private base stations (BS) can support connectivity for different spectrum bands (sub-GHz, 1 to 6 GHz, or mmWave). The 5G base station products must pass all of the test requirements prior to their release. Otherwise, the products are not 3GPP-compatible or appropriate to implement in a network.
What is 5G NR BS?
5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB. These 5G NR BS operate in two frequency ranges: FR1 and FR2. (../../assets/5G-NR-BS-Channel-Bandwidths.jpg). Table 1: Frequency Ranges
What is a 5G base station?
The goal of 5G networks is to achieve ultra-low latency (as low as 1 ms) and large-scale device connections (up to a million devices per square kilometer). Base station chips must support high-density small cell deployments, meet the massive device access demand, and emphasize high processing speeds and scheduling capability.
What are the technical requirements for 5G base station chips?
As core components, 5G base station chips must meet the following key technical requirements: 1.High Spectrum Efficiency and Large Bandwidth Support 5G networks use a broader range of spectrum resources, particularly the millimeter-wave bands (24 GHz and above).
Are 5G base station chips compatible with 4G & 6G networks?
5G base station chips must be compatible with 4G, 5G, and future 6G networks, supporting multi-band and technology standard switching to ensure seamless connection between generations of networks.
Learn More
- 5g emergency communication command base station
- Tbilisi 5G communication base station wind and solar complementary battery
- HJ Communication 5G base station is recognized by the state
- Communication 5G base station energy storage cabinet price
- Baghdad 5g communication base station inverter grid-connected energy storage
- 5g communication base station flow batteries are blocked by community residents
- Cameroon 5MWH liquid-cooled communication 5g base station
- Communication 5g small home base station settings
- Communication 5g and 5g base station
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
