
Inverter vs converter: What''s the difference?
Mar 29, 2024 · The fundamental difference between inverters and converters can be found in their functionality. Converters change the voltage of an electrical power source and can convert AC

Can An Inverter Convert AC To DC?
Jan 9, 2024 · Can An Inverter Convert AC To DC?Introduction: Inverters are electronic devices that convert DC (direct current) electricity into AC (alternating current) electricity. This is useful

How Does an Inverter Convert AC to DC
Jan 23, 2025 · Learn the process of how an inverter converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) efficiently. Inverters play a vital role in converting AC to DC and vice versa,

Convert AC Motor To DC Motor: Tips, Techniques, And
Apr 17, 2025 · To convert an AC motor to use a DC source, connect an inverter. The inverter changes DC voltage into AC. Keep in mind that universal motors can work with both AC and

DC and AC Inverters: What You Need to Know
Mar 20, 2025 · On the other hand, an AC to DC inverter does the reverse, converting AC power into DC to charge batteries or power DC devices. In simple terms, a DC to AC inverter allows

Can An Inverter Convert AC To DC?
May 19, 2025 · In summary, an inverter cannot convert AC power to DC power. The process of converting AC power to DC power requires a different type of electronic device called a rectifier.

The Main Differences Between Inverters and Converters
Dec 12, 2024 · Conversely, a converter is a device that changes electrical power from one form to another. Unlike an inverter, which changes DC to AC explicitly, a converter can perform

Inverters and Rectifiers: How to Convert DC to
Jun 29, 2025 · Learn how inverters and rectifiers can change the type of electric current and why they are essential for many applications in renewable energy,

Difference Between Inverter and Converter –
May 22, 2025 · In this article, we''ll explain how inverters and converters work, their unique roles, and how to choose the right one for your home, vehicle, or
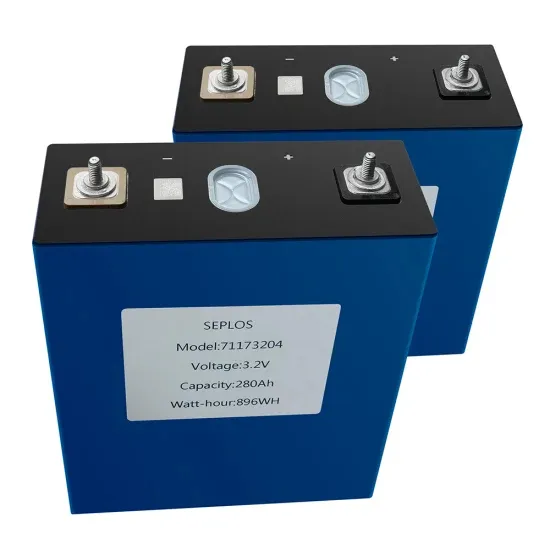

DC and AC Inverters: What You Need to Know
Mar 20, 2025 · DC and AC inverters are essential components in today''s energy systems. Whether you''re harnessing the power of the sun with solar panels, working with backup power
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
May 28, 2024 · This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC

An advanced guide to Understanding DC to AC inverters
Apr 4, 2024 · Yes! Knowing the difference will help you understand energy efficiency better and may even save you some money. Understanding the concept also allows you to recognize the

6 FAQs about [Can an inverter convert AC to DC ]
What is the difference between an inverter and a DC converter?
In contrast, an inverter is a specific type of converter that converts DC into AC. The primary function of an inverter is to allow devices that operate on AC power to use DC power sources, like batteries or solar panels. There are various applications of inverters, including:
Does an AC to DC inverter exist?
An AC to DC inverter is a bit of a misnomer, as traditional inverters actually convert DC power (like the kind you'd get from a battery or solar panel) into AC power, which is the standard type of power used in most commercial and industrial settings. In saying that, an AC to DC inverter technically doesn’t exist. What is an AC to DC Converter?
What are inverters & converters?
Inverters and converters are two important power electronics components that play a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), and vice versa. What’s the difference between AC vs DC? AC and DC are two different types of electrical current that are used in different power applications.
What is AC to DC converter?
It can also refer to a device that converts the type of electrical current from AC to DC or vice versa, but these are more specifically known as AC to DC converters (rectifiers) and DC to AC converters (inverters). Converters essentially adjust the power to a level that is compatible with a specific device or appliance.
Should I use a converter or an inverter?
The decision hinges on your specific power conversion needs: inverters are typically used for transforming DC to AC and back to DC, often for specialized applications. On the other hand, converters are fundamental in directly converting AC to a usable DC form.
Do I need an AC to DC converter?
It’s actually a fairly simple decision. If your device operates on DC power and you have an AC power source, you'll need an AC to DC converter. This is common in most industrial and commercial environments where equipment requires a stable DC power supply but is connected to an AC grid.
Learn More
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
