
Ito Coated Glass Vs. Ito Coated Flexible Pet Sheet
Nov 25, 2017 · The ITO coated glass may find a wider variety of applications, but the ITO coated flexible PET sheet cannot replace flexible display applications. With Techinstro, you can order

Influence of the Transparent Conductive Oxide
Dec 8, 2023 · In inverted perovskite solar cells (PSCs), indium tin oxide (ITO) is the most commonly used transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layer for coating

Alternative Transparent Conductive Oxides (TCO) to ITO
Mar 6, 2023 · The conductivity of ITO on typical plastic substrates is about 4X lower than on glass [3] and is affecting the performance of flexible displays, electronics and roll-to-roll coated PV

The Application of ITO Glass in Photovoltaic Cells – Demo
Conclusion: In conclusion, ITO glass plays a pivotal role in advancing the efficiency and performance of photovoltaic cells. Its application as a transparent conductive electrode,

Do you know the difference between FTO glass and ITO glass
Jul 30, 2025 · Do you know the difference between FTO glass and ITO glass? 1. In terms of definition, the composition of the coating layer of the two is different. ITO conductive glass

Conducting Glass
Mar 2, 2025 · The secret to creating conducting glass lies in applying a thin, virtually invisible layer of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) onto the glass surface. ITO is a unique material that exhibits both

What is the Difference Between Solar Photovoltaic Glass and Float Glass
Apr 15, 2023 · Photovoltaic glass is a special type of glass that converts sunlight into electricity by encapsulating solar cell modules in layers of glass. Usually low-iron tempered glass or double
Difference Between Ito And Fto Coated Glass | Techinstro
Apr 5, 2017 · The transparent conductive oxide TCO used to make conductive coating over a glass or flexible sheet. TCO such as Indium tin oxide (ITO) Coated Glass, Fluorine-doped tin

Influence of transparent conductive oxide layer on the
Oct 1, 2018 · PSCs using FTO-coated glass substrate did not show hysteresis in the I - V curves. However, hysteresis was caused using ITO-coated glass substrate, due to the slight

Difference Between Ito And Fto Coated Glass | Techinstro
Apr 5, 2017 · Here are the following comparisons between ITO coated glass and FTO coated glass. · There is a passivation layer on the glass surface, then ITO coated on the passivation

6 FAQs about [The difference between ito conductive glass and photovoltaic glass]
What is the difference between FTO glass and ITO conductive glass?
FTO conductive glass and ITO conductive glass seems to be a pair of twins, the name is only a difference of one character, but also are a kind of conductive glass. So, you may ask: what is the difference and connection between FTO glass and ITO glass, can they replace each other?
What is ITO conductive glass?
1, definition-wise, the two have different coating layer compositions. ITO conductive glass refers to the sodium-calcium-based or silicon-boron based substrate glass on the basis of the use of magnetron sputtering method coated with a layer of indium tin oxide film processed glass.
What is the difference between ITO coated and FTO coated glass?
In research and industry mainly ITO and FTO coated glass used. Here are the following comparisons between ITO coated glass and FTO coated glass. · There is a passivation layer on the glass surface, then ITO coated on the passivation layer. · FTO-coated glass is cheaper as compared to ITO glass.
Are PSCs with ITO coated glass better than FTO-coated glass?
The PSCs with ITO-coated glass achieved the 10.8% conversion efficiency, which is higher than that with FTO one (9.0%). The first finding is that the PSCs with ITO-coated glass substrate has lower resistances in series and parallel than those with ITO coated one.
Why is FTO glass better than ITO glass?
The etching process for FTO glass is easier compared to ITO glass. This means that FTO glass has relatively higher processing efficiency. FTO glass exhibits better resistance to high temperatures than ITO and can withstand temperatures up to 700 degrees. This implies that FTO glass offers greater stability in high-temperature environments.
What is FTO conductive glass?
ITO conductive glass refers to the sodium-calcium-based or silicon-boron based substrate glass on the basis of the use of magnetron sputtering method coated with a layer of indium tin oxide film processed glass. FTO conductive glass refers to fluorine-doped tin dioxide conductive glass.
Learn More
- The difference between photoelectric glass and photovoltaic glass
- The difference between single glass and double glass panels for photovoltaic panels
- French photovoltaic conductive glass
- Maputo Photovoltaic Conductive Glass
- Which company has photovoltaic glass in Comoros
- Huawei photovoltaic module ultra-hard glass
- How much is the photovoltaic glass factory in Greece
- Is a photovoltaic glass factory a photovoltaic factory
- What is the size of the photovoltaic glass in Conakry
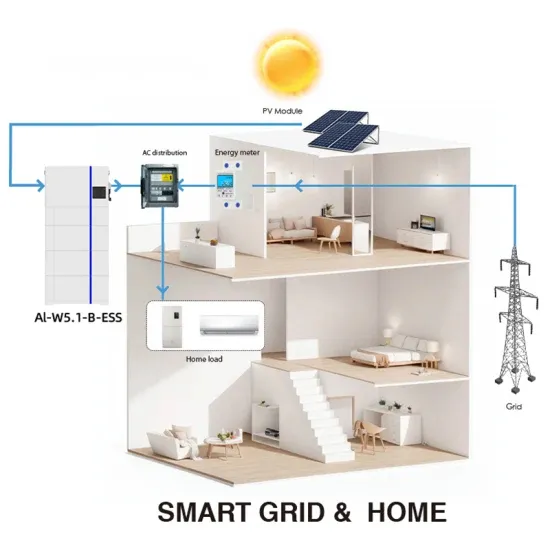
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
