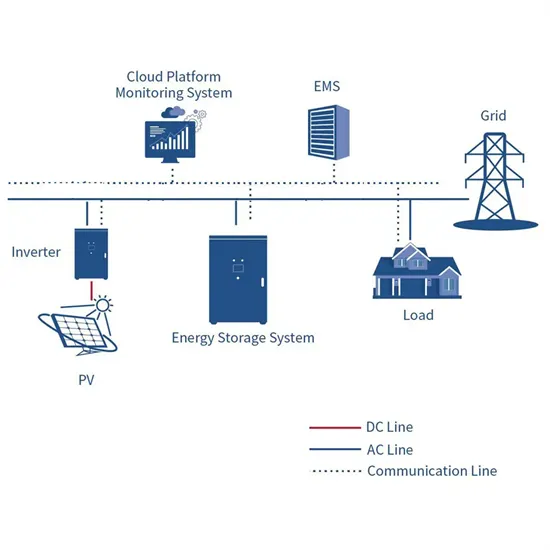
Base Station System Structure
Jan 28, 2011 · 2 Base Station Background The intent of this section is to explore the role of base stations in communications systems, and to develop a reference model that can be used to

Mobile Communication Network Base Station Deployment
Apr 13, 2025 · This paper discusses the site optimization technology of mobile communication network, especially in the aspects of enhancing coverage and optimizing base station layout.

huawei base station
Dec 23, 2023 · A base station, also known as an eNodeB (for 4G LTE) or gNodeB (for 5G NR) in Huawei''s terminology, is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between

International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering
Oct 26, 2021 · Base Station is the basic unit between the mobile switching center and the users. In the last two decades there is an immense growth in the world of mobile communications.

LTE Network Architecture
Jan 1, 2025 · What is Base Transceiver Station? A Base Transceiver Station (BTS) is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between a mobile device and a network.

Energy‐Efficient Base Stations | part of Green Communications
Aug 29, 2022 · With the explosion of mobile Internet applications and the subsequent exponential increase of wireless data traffic, the energy consumption of cellular networks has rapidly

Principle and Feature of Mobile Phone Signaling Data
Nov 17, 2024 · This chapter introduced the mobile communication principle, including the architecture and core technology of 4G-LTE mobile communication, the generation principle of
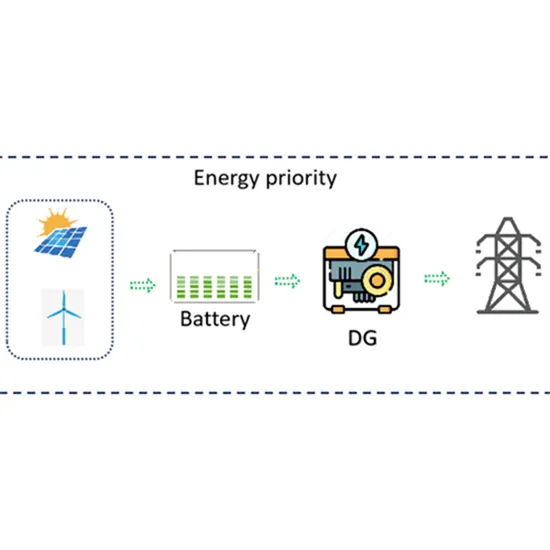
Design of a Magneto-Electric Dipole Element for
Jun 20, 2011 · The design of a conical beam wideband antenna with horizontal polarization is also described. These antennas have practical applications in
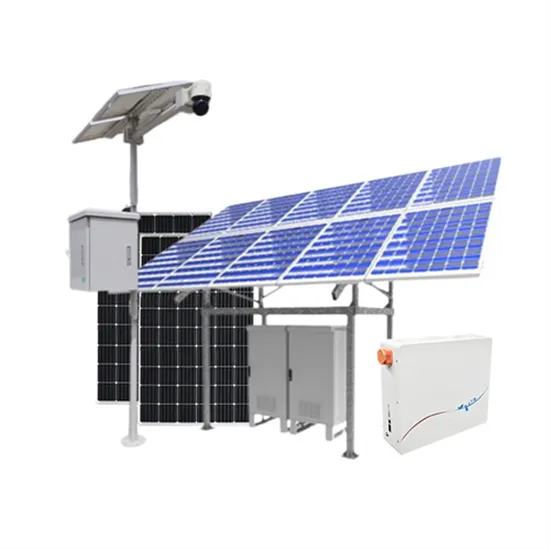

Understanding the Base Station Subsystem: A
Oct 4, 2024 · In the world of mobile telecommunications, understanding the Base Station Subsystem (BSS) is paramount for grasping how our everyday communications function
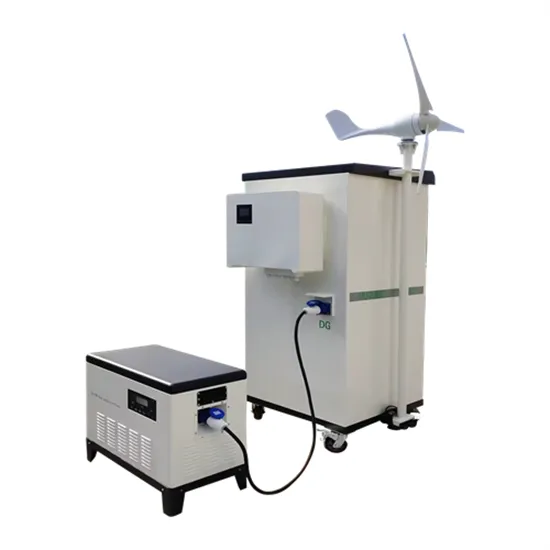

The Evolution of Base Station Antennas for Mobile Communications
Sep 21, 2007 · This paper gives a general overview of the design of base station antennas for mobile communications. It explains underlying theoretical and practical implementation

6 FAQs about [Mobile LTE base station communication principle]
How does LTE mobile work?
LTE Mobile communicates with just one base station and one cell at a time and there are following two main functions supported by eNB: The eBN sends and receives radio transmissions to all the mobiles using the analogue and digital signal processing functions of the LTE air interface.
Why are base stations important in cellular communication?
Base stations are important in the cellular communication as it facilitate seamless communication between mobile devices and the network communication. The demand for efficient data transmission are increased as we are advancing towards new technologies such as 5G and other data intensive applications.
What is a Base Transceiver Station (BTS)?
A Base Transceiver Station (BTS) is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between a mobile device and a network. Essentially, it acts as a bridge by transmitting and receiving radio signals. Understanding the technical components of a BTS can demystify how mobile communication works.
What is a mobile equipment for LTE?
The internal architecture of the user equipment for LTE is identical to the one used by UMTS and GSM which is actually a Mobile Equipment (ME). The mobile equipment comprised of the following important modules: Mobile Termination (MT) : This handles all the communication functions. Terminal Equipment (TE) : This terminates the data streams.
What are the components of LTE network architecture?
The high-level network architecture of LTE is comprised of following three main components: The User Equipment (UE). The Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN). The Evolved Packet Core (EPC).
What are the components of a base transceiver station?
Base Transceiver Stations consist of several components working in harmony. This section explores the major components of BTS, focusing on their functions and importance. Antennas and towers are fundamental to the operation of a BTS. Antennas are responsible for transmitting and receiving radio signals.
Learn More
- Mobile base station communication principle
- Technical requirements for base station equipment of LTE digital cellular mobile communication network
- Wind power principle of Lome communication base station inverter grid connection
- Mobile communication base station backup power supply
- Mobile communication base station rectifier power supply
- Photovoltaic principle of communication base station
- Working Principle of Wireless Communication Base Station Battery Energy Storage System
- Sao Tome and Principe LTE emergency communication base station flow battery supplier
- Communication base station energy storage battery pack principle
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
