
El Salvador Type Approval | Latin America Regulatory
LARCG COVERS LATAM SIGET Type Approval in El Salvador SIGET (Superintendencia General de Electricidad y Telecomunicaciones) is the telecommunications regulating agency

TOP SOLAR INVERTER SUPPLIERS IN EL SALVADOR
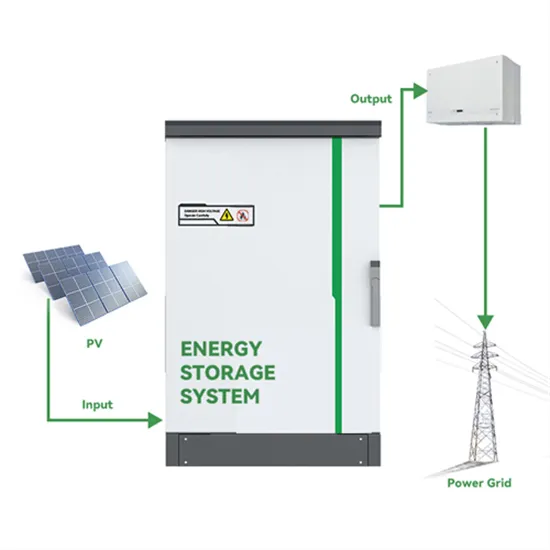
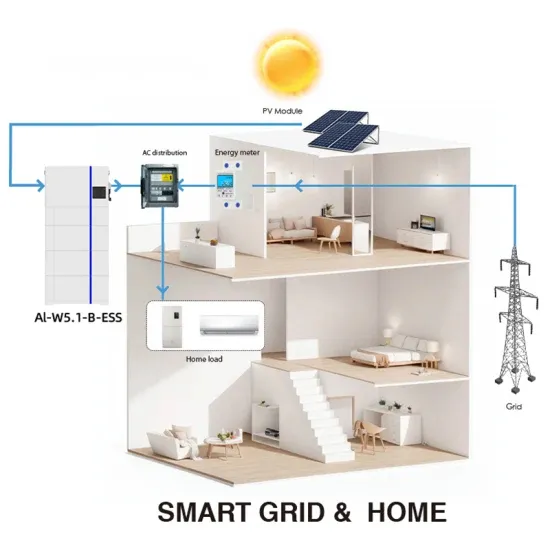
Solar panel with battery storage El Salvador We innovate with solar photovoltaic plant design, engineering, supply and construction services, contributing to the diversification of the energy

A review of renewable energy based power supply options for telecom
Jan 17, 2023 · Moreover, information related to growth of the telecom industry, telecom tower configurations and power supply needs, conventional power supply options, and hybrid system
List of Mobile Operators in El Salvador
Nov 4, 2023 · Mobile operators in El Salvador play a vital role in providing telecommunications services to the country''s population, facilitating connectivity, economic development, and

Portable solar power systems El Salvador
The upcoming projects in El Salvador include the construction of a Biogas Power Generation Plant on the Acelhuate River in San Salvador, the commissioning of a photovoltaic plant at the

Energy profile: El Salvador
Aug 18, 2025 · The 2020 fuel mix of El Salvador. Source: SIGET In 2020, imported fossil fuels accounted for the majority of El Salvador''s total energy supply, followed by smaller

Renewables Readiness Assessment: El Salvador
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY El Salvador depends heavily on fossil fuels to meet its energy needs for industry, transport and, to a certain extent, power generation. Increasingly, the country also

Optimum sizing and configuration of electrical system for
Jul 1, 2025 · The rising demand for cost effective, sustainable and reliable energy solutions for telecommunication base stations indicates the importance of integr
Spain''s watchdog reviews grid voltage control
Jun 19, 2025 · Spanish competition and energy watchdog said on Thursday it has updated the rules establishing power grid voltage control obligations for power

SOLAR ENERGY IN EL SALVADOR
El Salvador plus power energy The regulatory entities for the electricity sector in El Salvador are: • The Electrical Energy Directorate (DEE - Dirección de Energía Eléctrica), created in 2001, is

Nuclear Research Reactor to Lead El Salvador''s Seven-Year Energy
Oct 22, 2024 · When questioned about the cost of a nuclear power plant, Álvarez explained that the ongoing seven-year planning process would help provide answers. The size and type of

Green Hydrogen Innovation Centre | International Solar
El Salvador''s hydrogen sector is in its early stages, with limited production and consumption capacity and is mainly limited to industrial applications. The country''s abundant renewable

Energy Sector Guide 2023
May 21, 2024 · the maintenance and expansion of the electric power transmission system in a timely and effective manner, to guarantee the continuity of the electric supply in El Salvador in
Power Quality Standards and Regulations in El Salvador:
Nov 10, 2023 · The regulatory entity in EI Salvador, SIGET (General Superintendence of Electricity and Telecommunications of EI Salvador), published in 2004 a specific power quality

Geothermal and Solar Power Help Drive El Salvador''s Green Energy
Aug 7, 2025 · Geothermal and Solar Power Help Drive El Salvador''s Green Energy Growth. El Salvador sourced 65.01% of its electricity demand from renewable energy in June, according

REGULATION OF THE LAW OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS
Sep 20, 2012 · RATING PLAN: It is the fundamental technical plan adopted by an operator that determines the technical modality used as the base for charging the subscribers using a

Siget issues a new technical regulation to characterize
Jul 21, 2024 · The General Superintendency of Electricity and Telecommunications of El Salvador (SIGET) has issued the Technical Regulations to Characterize Projects that Take Advantage

El Salvador Transforms its Energy Matrix
Oct 14, 2015 · Finally, it is important to note that El Salvador will continue to work on adjusting its current regulations to enhance conditions conducive to increased penetration of clean energy

Hydroelectric Power Generation Reaches 20-Year High in El Salvador.
Sep 24, 2024 · Hydroelectric power plants in El Salvador generated 346.84 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of electricity in August, marking their highest monthly output in over two decades, according to

Nuclear Energy: El Salvador''s Path to a Stable
Oct 10, 2024 · El Salvador is set to develop its first nuclear research reactor by 2030, a significant step in the country''s energy transition. During a recent

6 FAQs about [El Salvador Telecommunication Base Station Inverter Power Generation Regulations]
Who regulates telecommunications in El Salvador?
SIGET (Superintendencia General de Electricidad y Telecomunicaciones) is the telecommunications regulating agency in El Salvador. Products that utilize Radio Frequency, Cellular, or Satellite technology require approval and certification in order to commercialize in El Salvador.
Which countries are connected to El Salvador's electricity grid?
El Salvador’s grid is interconnected with six regional neighbors – Belize, Costa Rica, Panama, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua – through the Central American Electrical Interconnection System (SIEPAC).
What is a telecommunication law in El Salvador?
Decreto no. 142: Ley de Telecomunicaciones (Telecommunication Law): defines technical standards for approvals and assigns bands of operations for use in El Salvador. Decreto no. 372: Reforma a la Ley de Telecomunicaciones (Updates to Telecommunication Laws) updates standards for concession for use of bands of frequencies in El Salvador.
Does El Salvador have a capacity to conduct renewable projects?
El Salvador has the national, political will to conduct renewable projects, as evidenced by the numerous incentives provided, the dire climate risks in the country, and their regional partnerships. While the institutional capacity is still catching up, to say they don’t have any capacity would be false.
Should El Salvador prioritize renewables?
Prioritizing renewables is of utmost priority to El Salvador from an energy security basis, as they do not have any domestic oil, gas or coal supply and are dependent on imported fossil fuels from their partners.
Does El Salvador have a telecommunication sector?
El Salvador’s telecommunication sector has operated under a privatized legal and institutional framework since 1997, encouraging competition in most areas and allowing foreign investment.
Learn More
- San Salvador Communication Base Station Inverter Photovoltaic Power Generation Tender
- What is the situation in El Salvador Telecommunication base station inverter
- How is the photovoltaic power generation of the Sri Lanka communication base station inverter
- Belmopan Telecommunication Base Station Lead Acid Battery Power Generation Company
- Morocco communication base station inverter grid-connected photovoltaic power generation quotation
- Stockholm communication base station inverter grid-connected photovoltaic power generation system
- East Asia Communication Base Station Inverter Grid-connected Photovoltaic Power Generation Quotation
- Base station outdoor integrated cabinet base station power generation
- Communication base station energy storage power generation equipment
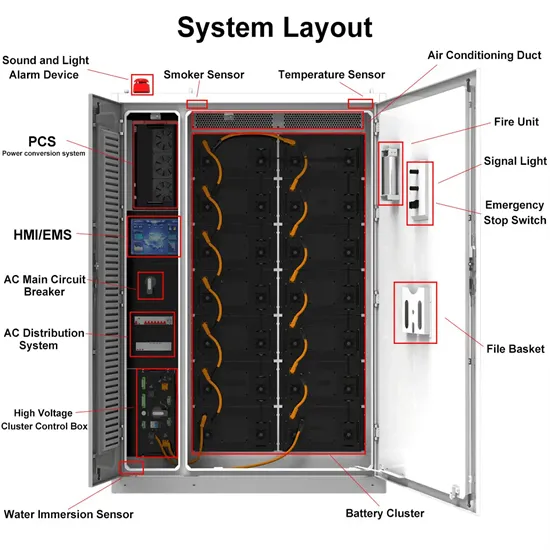
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
