
Grid Connected Inverter Reference Design (Rev. D)
May 11, 2022 · Description This reference design implements single-phase inverter (DC/AC) control using a C2000TM microcontroller (MCU). The design supports two modes of operation

Grid-connected isolated PV microinverters: A review
Jan 1, 2017 · Galvanic isolation in grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) microinverters is a very important feature concerning power quality and safety issues. However, high-frequency

Modeling and Implementation of Grid Following and Grid
Dec 4, 2022 · An efficient way to lessen the burden on the grid is by deploying micro-grids to offer local power to consumers. The issues associated by such micro-grids are power quality, load

Study of Seamless Microgrid Transition Operation Using
Oct 20, 2023 · Goal of this work: Study operational techniques to achieve seamless microgrid transitions by dispatching a GFM inverter. We propose three techniques and compare them

A Novel Inverter Control Strategy with Power Decoupling for
May 10, 2025 · In islanded mode, the proposed model can provide virtual inertia and damping properties, while in grid-connected mode, the inverter''s active power output can follow the

Inverter Control for Grid Connected and Islanding Mode
Dec 6, 2016 · A micro grid which contains (DG) operates while connected to the grid, but in case of outages it operate independently without the grid. In this paper we are going to simulate and
Grid-Forming Inverters for Grid-Connected Microgrids:
Mar 4, 2022 · The electric power grid is in transition. For nearly 150 years it has supplied power to homes and industrial loads from synchronous generators (SGs) situated in large, centrally

Grid-Forming Inverters in a Microgrid: Maintaining Power
Jan 20, 2024 · This article presents an autonomous control architecture for grid-interactive inverters, focusing on the inverters providing power in a microgrid during utility

[2505.06664] A Novel Inverter Control Strategy with Power
May 10, 2025 · In islanded mode, the proposed model can provide virtual inertia and damping properties, while in grid-connected mode, the inverter''s active power output can follow the

A grid-connected single-phase photovoltaic micro inverter
Nov 1, 2017 · In this paper, the topology of a single-phase grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) micro-inverter is proposed. The PV micro-inverter consists of DC-DC stage with high voltage gain

Grid-Connected Solar Microinverter Reference Design
Oct 28, 2010 · Grid-Connected Solar Microinverter Reference Design Software Integration Summary In this webinar, we will go through the design of Microchip''s Grid-Connected Solar

Grid-Connected Solar Microinverter Reference Design
Nov 29, 2011 · There are two main requirements for solar inverter systems: harvest available energy from the PV panel and inject a sinusoidal current into the grid in phase with the grid

ngerulmud energy storage for grid stability
A critical evaluation of grid stability and codes, energy storage This was expanded in Hernández [53] considering the application of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) with hybrid energy storage

Control of Grid-Connected Inverter | SpringerLink
May 17, 2023 · The control of grid-connected inverters has attracted tremendous attention from researchers in recent times. The challenges in the grid connection of inverters are greater as

Grid-connected Solar Micro Inverter | Renesas
4 days ago · The solar micro inverter system based on renewable energy is becoming increasingly popular among consumers. Each system unit operates with only tens of volts of

Inverter-based islanded microgrid: A review on
Jan 1, 2022 · An inverter-based MG consists of micro-sources, distribution lines and loads that are connected to main-grid via static switch. The inverter models include variable frequencies as

Grid Forming Inverters: EPRI Tutorial (2021)
As present-day IBR control methodology may not be sufficient to ensure grid security in a future inverter dominated system, grid-forming inverter control technology has been discussed in

MICROINVERTER TOPOLOGIES FOR SOLAR PV-GRID
Aug 5, 2021 · Here there is a detailed review on different topologies of micro-inverter for grid tied solar PV, their merits and demerits. This also includes the element or the components involved

Grid Connected Inverter Reference Design (Rev. D)
May 11, 2022 · High-efficiency, low THD, and intuitive software make this design attractive for engineers working on an inverter design for UPS and alternative energy applications such as

Research and design of a dual buck micro grid-connected inverter
May 28, 2025 · In light of the experiences gained from previous micro grid-connected inverters, a dual Buck micro grid-connected inverter based on a small signal model is proposed. The front

Research and design of a dual buck micro grid-connected inverter
Apr 1, 2025 · In light of the experiences gained from previous micro grid-connected inverters, a dual Buck micro grid-connected inverter based on a small signal model is proposed. The front

Grid-Connected Micro Solar inverter Implement Using a
Apr 1, 2023 · This paper describes how to use a TMS320F2802x to design a micro solar inverter with low cost and high performance. Also discussed is the use of the interleaved active-clamp

A Three-Phase Grid-Connected Micro-Inverter for AC
Nov 16, 2017 · The proposed micro-inverter consists of a flyback stage, a third-harmonic injection circuit and a line-commutated current-source type inverter. The flyback stage realizes
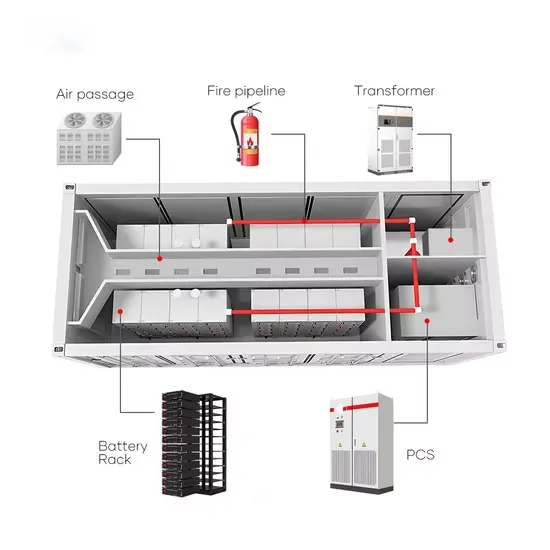
6 FAQs about [Ngerulmud Micro Grid-connected Inverter]
What should a user not do when using a grid connected inverter?
The user must not touch the board at any point during operation or immediately after operating, as high temperatures may be present. Do not leave the design powered when unattended. Grid connected inverters (GCI) are commonly used in applications such as photovoltaic inverters to generate a regulated AC current to feed into the grid.
What is a grid-connected solar microinverter system?
A high-level block diagram of a grid-connected solar microinverter system is shown in Figure 4. The term, “microinverter”, refers to a solar PV system comprised of a single low-power inverter module for each PV panel.
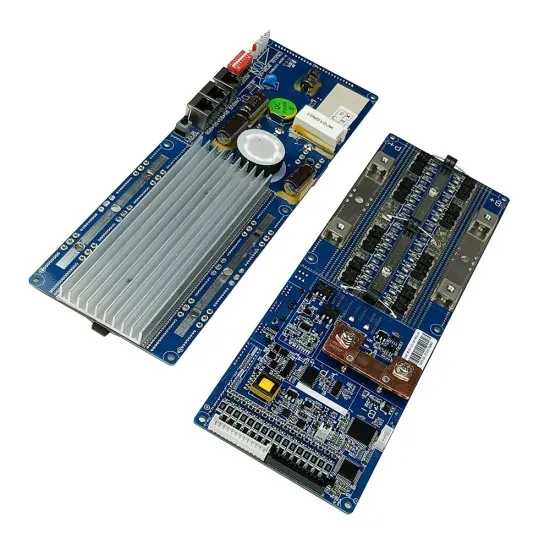
What is the control design of a grid connected inverter?
The control design of this type of inverter may be challenging as several algorithms are required to run the inverter. This reference design uses the C2000 microcontroller (MCU) family of devices to implement control of a grid connected inverter with output current control.
Are inverters able to inject real power into a grid?
Inverters have assumed that the grid is strong and will provide a stable and clean voltage and that they are able to inject real power into the grid without undue impact on its operation. References is not available for this document. Need Help?
Can a grid connected inverter be left unattended?
Do not leave the design powered when unattended. Grid connected inverters (GCI) are commonly used in applications such as photovoltaic inverters to generate a regulated AC current to feed into the grid. The control design of this type of inverter may be challenging as several algorithms are required to run the inverter.
What happens if a microinverter is not able to detect a grid shutdown?
In the event that the local load resonates near the operating frequency before the grid was removed, the microinverter will see a small change in active and reactive power, and will not be able to detect that the grid has shut down. This is known as an island condition and is a Non-Detection Zone (NDZ) for the microinverter.
Learn More
- Berlin Micro PV Grid-connected Inverter
- 500w micro grid-connected inverter
- Grid-connected micro inverter supplier
- Communication base station inverter grid-connected battery detection principle
- Uzbekistan 5g communication base station inverter grid-connected body
- CIGS photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
- Bangkok communication base station inverter grid-connected manufacturer
- Malaysia Penang PV grid-connected inverter
- Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter for temporary use
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
