
Difference Between UPS and Inverter | Kondaas
Apr 26, 2013 · Use a UPS for critical electronics that can''t afford a second of delay, and a high-capacity inverter to power essential household devices. In

IPS vs UPS: What''s the Difference and Which Do
Apr 18, 2024 · UPS is a device that provides immediate alternative power supply to computers or other electric or electronic devices. When it comes to buying

Home UPS vs. Traditional Inverters: Which is Right for You?
Choosing between a Home UPS and a traditional inverter can be challenging, as both have unique features and benefits. In this blog, we''ll explore the differences between Okaya''s Home

Difference between UPS and Inverter – Which is better?
Jan 10, 2025 · A UPS offers better protection and responsiveness for sensitive applications, while an inverter provides longer-lasting power for less critical loads. Understanding your unique

Best inverter companies in India 2025: Top 10
Apr 9, 2025 · Fed up with constant power cuts? Explore top-rated inverters from the best companies in India and enjoy reliable power backup for your home or

UPS or Inverter: Which Is Best for Home? | Comparison
Jan 14, 2025 · To answer the crucial question, "UPS or inverter which is best for home?", let''s explore the key differences: Immediate switch-over during power outages with no noticeable

Best inverter batteries: Top 10 picks for power
Mar 6, 2025 · Explore the 10 best inverter batteries for reliable backup, ensuring efficiency, durability, and long-lasting performance for homes and offices.

Comparison Between UPS And Inverter
Nov 18, 2024 · Understanding the difference between UPS and inverter systems is crucial for choosing the right power backup solution. While UPS provides instant power during outages,
Best Home Ups Or Inverter [Updated: August 2025]
Aug 2, 2025 · Compared to the bulkier OPTI-UPS DS3000E, the TS2000E is lighter, quieter, and easier to set up, making it a smarter choice for home use. Best home ups or inverter: Our Top
Difference Between UPS and Inverter | What Should I Choose?
Explore the disparities between UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) and inverters, unraveling the complexities of each. Discover the key factors to consider in choosing between them for your

What Is the Difference Between Inverter Mode
Sep 6, 2024 · Most hybrid and smart inverters have UPS mode to take advantage of that. UPS Mode, on the other hand, is indispensable for critical applications

6 FAQs about [Which is better for home use UPS or inverter ]
What is the difference between a ups and an inverter?
When it comes to ensuring uninterruptible power supply for your home, the debate between UPS and inverter has been ongoing. Both serve the purpose of providing backup power during outages, but they differ in their functionality and applications.
Should I use an ups or an inverter?
If you require a portable power source for outdoor activities, RVs, or off-grid living. In summary, the choice between a UPS and an inverter hinges on your specific needs. A UPS offers better protection and responsiveness for sensitive applications, while an inverter provides longer-lasting power for less critical loads.
What is an inverter used for?
It is often used to power electrical appliances from energy sources such as batteries or solar panels. Unlike a UPS, an inverter does not store energy but only converts it. It can be used alone or integrated into a more complex power system, such as a UPS, to provide backup power during outages.
How does an inverter ups work?
Residential and commercial applications, especially in areas with unreliable grid power or for off-grid use. In the inverter UPS mode, the electrical load is directly powered by the utility grid or another power source, bypassing the inverter's DC to AC conversion process. The battery only discharges during outages.
Do you need a power supply or inverter?
When it comes to keeping your home running at all times, you need reliable energy in order to keep appliances, computers, and other devices operating without interruption. The two most popular options for uninterrupted power flow are uninterruptible power supply (UPS) and inverters.
Should I buy an inverter?
Opt for an Inverter if: You’re looking for long-term backup during power outages. You want to run lights, fans, and basic appliances during blackouts. You’re okay with a few seconds of delay when the power goes out. Let's say you're writing your thesis (or watching K-dramas nonstop, no judgment) and the electricity shuts off.
Learn More
- Which inverter is better for photovoltaic use
- Which photovoltaic panel is better for home use
- Which is better sine wave or UPS inverter
- Which inverter is better for Swedish communication base station grid connection
- Which photovoltaic off-grid inverter is better
- Which one is better 12v inverter or 72v inverter
- Which is better lithium battery plus inverter or mobile power supply
- Inverter for home use 8000w
- Is it better to use 24V or 48V inverter
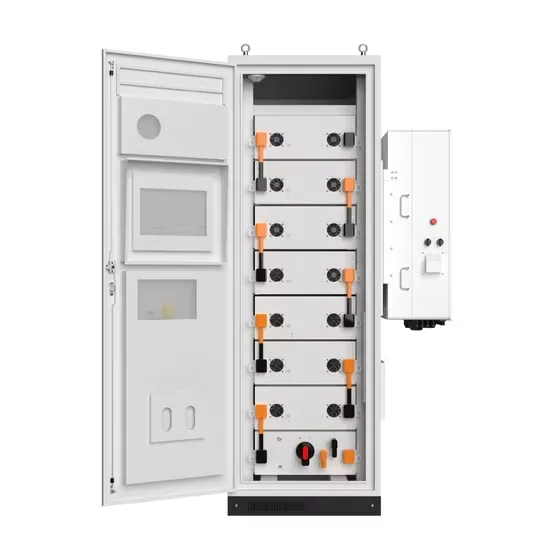
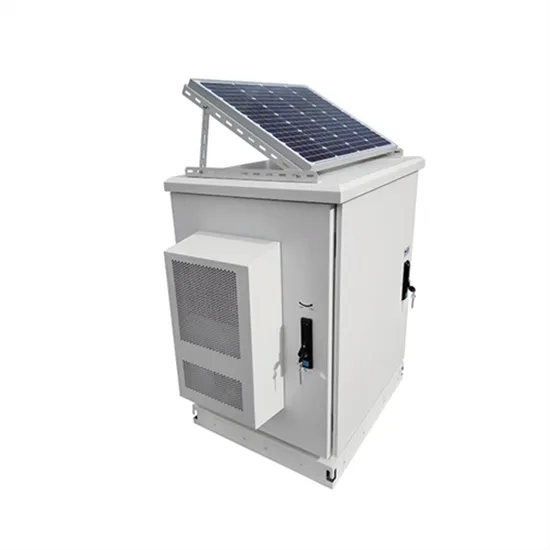
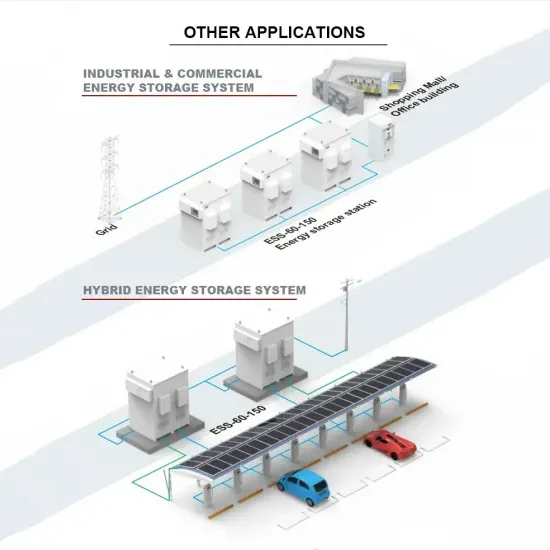
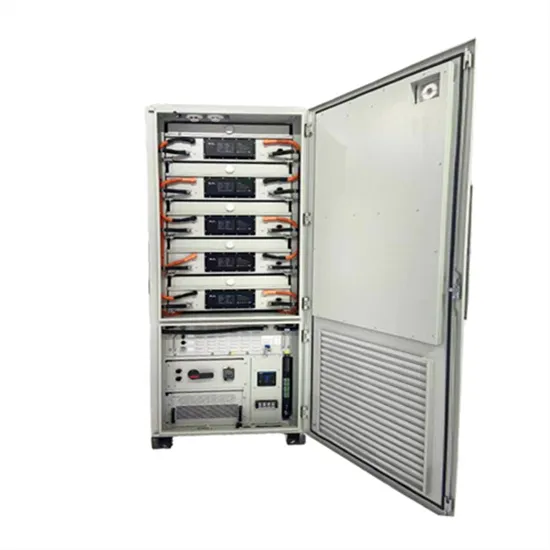
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
