
Half-Bridge vs. Full-Bridge: What is the Difference?
May 12, 2022 · Full-bridge inverters are more efficient than half-bridge inverters because they can utilize the entire DC voltage swing, from 0 volts to the peak

Full Bridge Inverter: Circuit, Waveforms, Working
Jun 2, 2025 · Single-phase inverters are classified into two types, i.e. half bridge inverters and full bridge inverters. In this session, I will be going to explain a

MODULE-3 INVERTERS Single phase voltage source
Mar 13, 2024 · the 40HZ, 50HZ, 60HZ frequencies as of our requirement. If the dc input is a voltage source the the inverter is known as VSI (Voltage Source Inverter). The inverters need

Single Phase Inverter : Types, Circuit with
Oct 30, 2023 · Single Phase Half-Bridge Inverter The single-phase half-bridge inverter circuit diagram is shown below. This circuit is designed with thyristors

Single Phase Full Bridge Inverter – Resistive Load
Jul 12, 2021 · Single phase full bridge inverter circuit required more component for conversion than that used in single phase Half bridge inverters so, the cost of

Single Phase Voltage Source Inverters
(b) (b) (a) A single-phase full bridge inverter is connected to an RL load. For a de source voltage of V, and output frequency f 1 IT, obtain expressions for load current as a function of time for
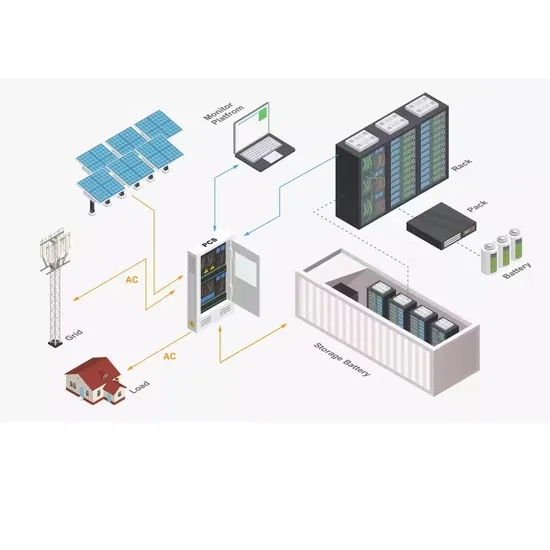
Lecture 23: Three-Phase Inverters
Feb 24, 2025 · In particular, considering "full-bridge" structures, half of the devices become redundant, and we can realize a 3-phase bridge inverter using only six switches (three half

Single Phase Inverter
Jul 23, 2025 · Single phase inverters are ideal for use in home appliances, power tools, office equipment, water pumping in agriculture, adjustable speed ac drives, induction heating,

DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF SINGLE PHASE
May 1, 2021 · There are two types of single phase inverters i.e. full bridge inverter and half bridge inverter, which are explained below. Half Bridge Inverter: The half bridge inverter is the basic

Half Bridge Inverter : Circuit, Advantages, & Its
8 rows · Thus, this is all about an overview of the half-bridge inverter, the difference between half-bridge inverter and full-bridge inverter, advantages,

Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter | Circuit, operation and
May 6, 2023 · Basically, there are two diferent type of bridge inverters: Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter and Single-Phase Full Bridge Inverter. Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter consists of

Single Phase Full Bridge Inverter | Power4all
Single-phase inverters can be further categorized as half-bridge inverters and full-bridge inverters. This article offers an extensive explanation of the construction and operational principles of a

Single Phase Half Bridge and Full Bridge Inverter
Nov 22, 2020 · There are mainly two types of single-phase inverter: Half Bridge Inverter and Full Bridge Inverter. Here we will study how these inverters can

[Solved] Modified McMurray full-bridge inverter
Jul 30, 2025 · A single-phase modified McMurray-Bedford full bridge inverter can be realized by connecting two half bridge inverters as shown in figure. The

Half H-Bridge Inverter – Circuit, Operation,
3 days ago · What is Half H-Bridge Inverter? Half H-bridge is one of the inverter topologies which convert DC into AC. The typical Half-bridge circuit consists of

LECTURE NOTES
Jan 3, 2020 · UNIT IV: INVERTERS Inverters – Single Phase Inverter – Basic Series Inverter – Basic Parallel Capacitor Inverter Bridge Inverter – Waveforms – Simple Forced Commutation

6 FAQs about [Single-phase half-bridge and full-bridge inverters]
What is single phase half bridge inverter?
Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter is a type of Single-Phase Bridge Inverter. It is a voltage source inverter. Voltage source inverter means that the input power of the inverter is a DC voltage Source. Basically, there are two diferent type of bridge inverters: Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter and Single-Phase Full Bridge Inverter.
What is the difference between half bridge and full bridge inverter?
Comparison between half and full bridge inverters have also been detailed. Single Phase Full Bridge Inverter is basically a voltage source inverter. Unlike Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter, this inverter does not require three wire DC input supply. Rather, two wire DC input power source sufices the requirement.
What is the power circuit of a single phase full bridge inverter?
The power circuit of a single phase full bridge inverter comprises of four thyristors T1 to T4, four diodes D1 to D1 and a two wire DC input power source Vs. Each diode is connected in antiparallel to the thyristors viz. D1 is connected in anti-parallel to T1 and so on.
How to control the output frequency of a single phase full bridge inverter?
Rather, two wire DC input power source suffices the requirement. The output frequency can be controlled by controlling the turn ON and turn OFF time of the thyristors. The power circuit of a single phase full bridge inverter comprises of four thyristors T1 to T4, four diodes D1 to D1 and a two wire DC input power source Vs.
How many types of single phase inverters are there?
There are two types of single phase inverters − full bridge inverter and half bridge inverter. This type of inverter is the basic building block of a full bridge inverter. It contains two switches and each of its capacitors has a voltage output equal to $\frac {V_ {dc}} {2}$.
What is a full bridge inverter?
In full bridge inverter, peak voltage is same as the DC supply voltage. The circuit diagram of full bridge inverter is as shown in below figure. The gate pulse for MOSFET 1 and 2 are same. Both switches are operating at same time. Similarly, MOSFET 3 and 4 has same gate pulses and operating at same time.
Learn More
- Single-phase full-bridge inverter parameter selection
- Differences between single-phase and three-phase inverters
- Single-phase hlH-bridge inverter structure
- Safety standards for inverters connected to the grid for mobile energy storage sites
- Factory price 3000w inverters in Dominica
- Inverters drive module prices
- Wholesale 1500 watt inverters in Panama
- Hot sale factory price 3000w inverters company
- Wholesale household inverters in Mongolia
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
