
What is the Peak Output Power of a Power Inverter?
May 25, 2022 · The power inverter itself consumes part of the power during operation, and its input power is higher than its output power. In other words, the efficiency of the power inverter

Inverter Peak Power vs Rated Power: What it is
Apr 21, 2025 · The rated power is the power at which the inverter is stabilized over a long period, whereas the peak power is only used for short periods of

A review on topology and control strategies of high-power inverters
Feb 15, 2025 · In large-scale applications such as PV power plants, "high-power" in medium voltage (MV) inverters is characterized by the use of multilevel inverters to enhance efficiency

Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They
Dec 17, 2019 · An inverter (or power inverter) is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage. While DC power is common
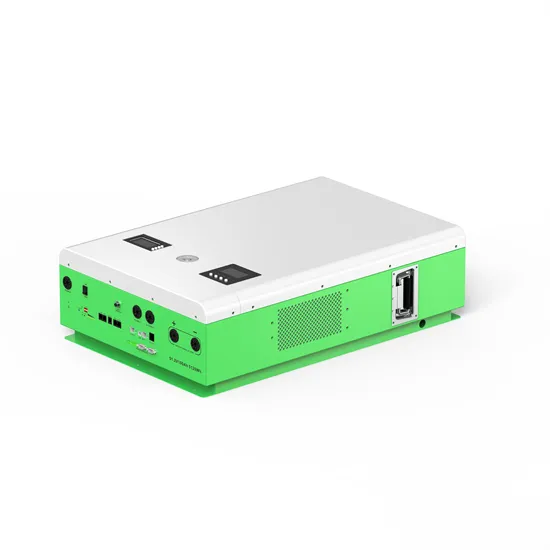

Inverter Power Calculator & Formula Online Calculator Ultra
Oct 3, 2024 · Common FAQs What does efficiency mean in the context of inverters? Efficiency refers to the percentage of input power that is converted to usable AC power. High-efficiency
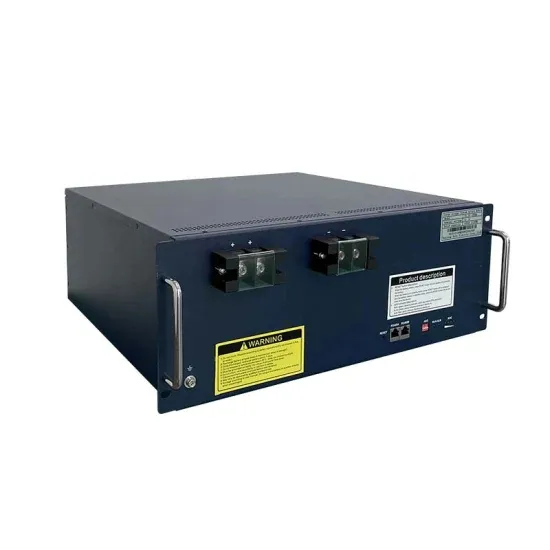

Unveiled! the truth about inverter acs: how many watts do
Aug 30, 2024 · This modulation allows for significant energy savings and improved efficiency. Factors Affecting Power Consumption The power consumption of an inverter air conditioner
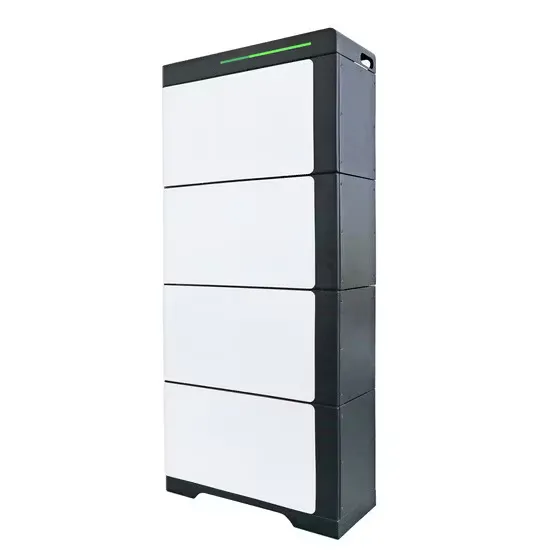

Differences between Central Inverter and String Inverter
Aug 29, 2019 · The power equipment and signal circuit are on the same panel, thus having difficult design and manufacturing, and poorer reliability. The inverter using the discrete power
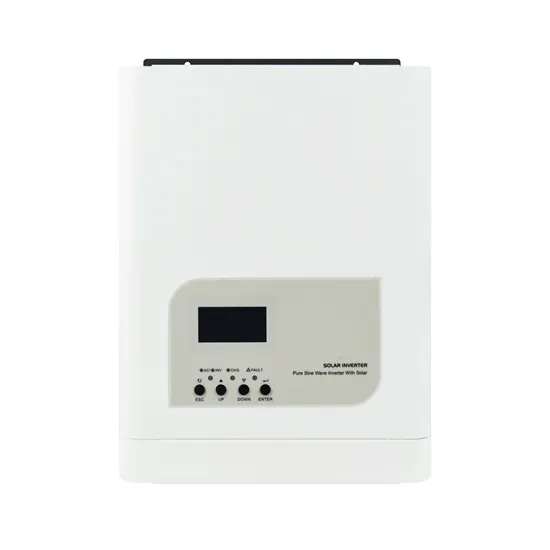

Efficiency of Inverter: Calculation & Equation Guide
Jun 22, 2022 · With a sine wave, most motors and many electrical appliances run more efficiently and consume less electricity. A modified sine wave will often require 15% to 20% more power

Are Large Inverters Less Efficient?
Jul 21, 2025 · Most modern inverters have efficiency ratings between 90% and 98%. Let''s break it down: If you feed 1000 watts of DC power into your inverter and it outputs 950 watts of AC
How Much Power Does Solar Inverter Use and How to
Aug 23, 2024 · Learn how much power a solar inverter uses and get practical tips on designing the ideal solar power project. From understanding inverter efficiency to system sizing, this

Four types of grid-connected inverter settings
Jul 30, 2025 · The grid-connected inverter settings in solar photovoltaic power generation systems are divided into: centralized, master-slave, Distributed and

Impact of inverter configuration on energy cost of grid-connected
May 1, 2012 · This paper proposes a method to evaluate and optimize inverter configurations for grid-connected PV systems. It is studied by Monte-Carlo analysis that how the inverter

How Much Power an Inverter Draws with No Load
How to Calculate Inverter No Load Current Draw The no load current is listed on the inverter specifications sheet. It will be either no load current draw (amps) or no load power (watts),

How much power does an Inverter use just sitting there idling?
Oct 30, 2020 · Thats going to depend on the hardware you have. Expensive units are typically more efficent (use less power when the load is off). My 3kw "inveter" is an all in one so it has a

Does a larger size inverter draw more energy from a battery
Aug 19, 2025 · Even though the "load" may be only 1000 watts, the inverter is creating the maximum watts of the inverter, and the inverter was drawing power from the batteries even if

On Grid Solar Inverter Power Configuration and Maintenance
Through an in-depth understanding of the power configuration and maintenance of on grid solar inverters, users can more effectively utilize solar resources, enhancing the economic benefits

6 FAQs about [Does the higher the inverter power configuration the more power it consumes ]
Why is a high power inverter more efficient?
Higher power inverters tend to have higher no load draw 4. Inverters do not have uniform efficiency across their whole power range (most but not all will be most efficient at or near their limit) 5. No inverter is more efficient than the most efficient inverter, so the more you can run directly from DC the less efficiency penalty you get hit with.
How much power does an inverter use?
The inverter has an 87% efficiency rating. Now take a 4000 watt inverter like the Energizer 4000 which uses about 25 watts in standby mode. Plug the same 35 watt fan into it and the inverter consumes 55 watts. Use the same steps as above. The efficiency rating is only 63%. But if you increase the load, efficiency goes up.
Does inverter size matter?
Well, size does matter, but there is more to it. An inverter uses 10% more power than its appliance load due to inefficiency and standby mode requirements. Inverter efficiency increases with a higher load, so they should always run close to full capacity.
What happens if inverter load is less than 15%?
In general, if the inverter is loaded less than 15%, the efficiency will be low. As a result, a good match between inverter capacity and load capacity will allow us to obtain more efficiency, which is more ac output power from the inverter for the same DC input power.
Are inverters too big?
Inverters play a crucial role in converting DC power to AC power, but choosing the right size is essential for optimal performance. In this article, we'll explore the potential implications of using an inverter that is too big for your power needs, shedding light on the effects and considerations associated with oversized inverters.
What is the highest efficiency point of an inverter?
The highest efficiency point is never at full flat out power as mentioned above by previous posters. Its probably at about 15% to 20% of rated power which can fit in very well with normal domestic load profiles. Many inverter manufacturers lie a little bit and quote the max rated power, and efficiency at the highest efficiency point.
Learn More
- The bigger the inverter the more battery power it consumes
- Wind power solar inverter
- Conakry inverter power
- Instantaneous power of photovoltaic inverter
- Xiaomi Outdoor Power Inverter
- Best configuration for outdoor power supply
- Wholesale 1500 power inverter in Kyrgyzstan
- Uninterruptible Power Supply and Inverter
- Power frequency pure sine wave inverter 2
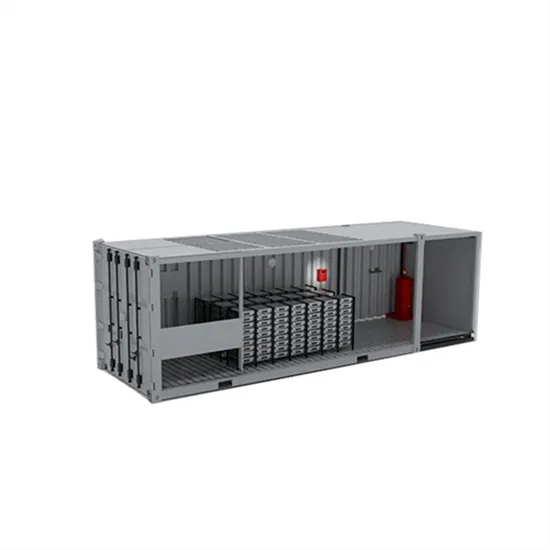
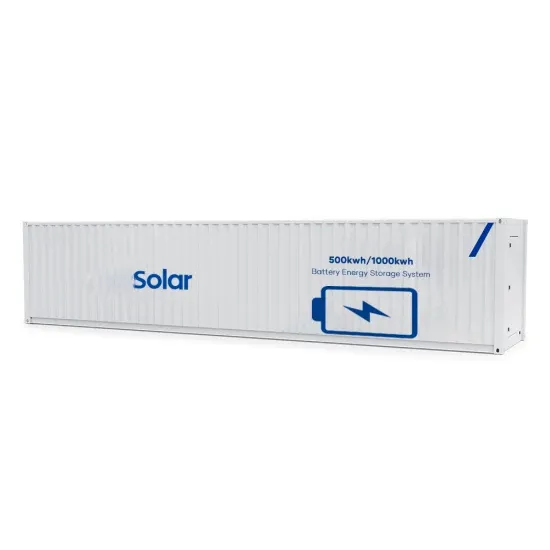
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
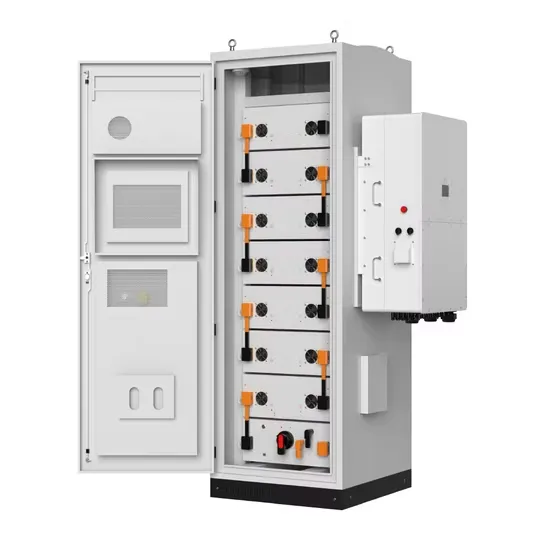
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
