
Mobile base station site as a virtual power plant for grid
Mar 1, 2025 · The base station has a 3*25 Ampere (A) grid connection and several generations of mobile networks, including LTE & 5G in different frequency bands. The maximum theoretical

Overview of power inverter topologies and control structures for grid
Feb 1, 2014 · In grid-connected photovoltaic systems, a key consideration in the design and operation of inverters is how to achieve high efficiency with power output for different power

Stability-Oriented Minimum Switching/Sampling Frequency
Oct 5, 2021 · Although the cyber-physical system stability is widely studied, scholars focus more on system stability with communication time delay. Therein, grid-connected i

Hybrid compatible grid forming inverters with coordinated
Aug 16, 2025 · This guarantees that the inverter maintains stable operation in both grid-connected and islanded modes, effectively supporting frequency regulation, voltage control, and power

SoC–Based Inverter Control Strategy for Grid-Connected
Jan 23, 2025 · The successful integration of battery energy storage systems (BESSs) is crucial for enhancing the resilience and performance of microgrids (MGs) and power systems. This study

Grid-Forming Inverters – Enabling the Next Generation
May 15, 2023 · Can heterogeneous systems containing GFL inverters, GFM inverters, and machines operate together to guarantee frequency regulation and stability?
Overview of technical specifications for grid-connected
Nov 15, 2017 · This paper compares the different review studies which has been published recently and provides an extensive survey on technical specifications of grid connected PV

A comprehensive review of grid-connected solar
Jun 1, 2023 · The state-of-the-art features of multi-functional grid-connected solar PV inverters for increased penetration of solar PV power are examined. The various control techniques of multi

Distributed Coordination of Grid-Forming and Grid-Following Inverter
Nov 19, 2024 · In this paper, we study the grid-level coordinated control of a mix of GFM and GFL IBRs for power system frequency regulation. By leveraging the projected primal-dual gradient

Distributed Coordination of Grid-Forming and Grid
May 13, 2025 · This paper studies grid-level coordinated control of grid-forming (GFM) and grid-following (GFL) inverter-based resources (IBRs) for scalable and optimal frequency control.

Power electronics in a PV-integrated grid-connected electric
Nov 25, 2024 · Power electronics in a PV-integrated grid-connected electric vehicle charging system for V2G/G2V operation | Control, Communication, Monitoring and Protection of Smart

Enhancement of power quality in grid-connected systems
Mar 7, 2025 · Enhancement of power quality in grid-connected systems using a predictive direct power controlled based PV-interfaced with multilevel inverter shunt active power filter

Solar Integration: Inverters and Grid Services Basics
4 days ago · If you have a household solar system, your inverter probably performs several functions. In addition to converting your solar energy into AC

Evaluation of Inverter-based Grid Frequency Support using Frequency
Aug 10, 2018 · Currently, the majority of grid-connected PV sources operate in current-control mode, which is known as grid-following control. The ability of grid-following so

Optimised configuration of multi-energy systems
Dec 30, 2024 · Optimised configuration of multi-energy systems considering the adjusting capacity of communication base stations and risk of network congestion

DESIGNING OF GRID CONNECTED INVERTER FOR PV
Jun 7, 2021 · Abstract – In recent years, photovoltaic (PV) systems are acquiring more popularity due to their ease of availability. The photo-voltaic system can be classified into grid-connected

Grid Forming Inverters: EPRI Tutorial (2021)
Abstract With the increasing penetration of renewable energy, inverter-based resources (IBRs) are gradually replacing synchronous generators as the new generation capacity. As present

Control strategies of parallel operated inverters in renewable
Nov 1, 2016 · In the distributed generation environment, parallel operated inverters play a key role in interfacing renewable energy sources with the grid or forming a grid. This can be achieved

Distributed Coordination of Grid-Forming and Grid-Following Inverters
May 13, 2025 · Abstract The large-scale integration of inverter-interfaced renewable energy sources presents significant challenges to maintaining power balance and nominal frequency

Synchronization in electric power networks with inherent
May 5, 2022 · Additionally, we report the feasibility of operating interconnected electric grids with up to 100% power contribution from inverter-based renewable generation technologies.

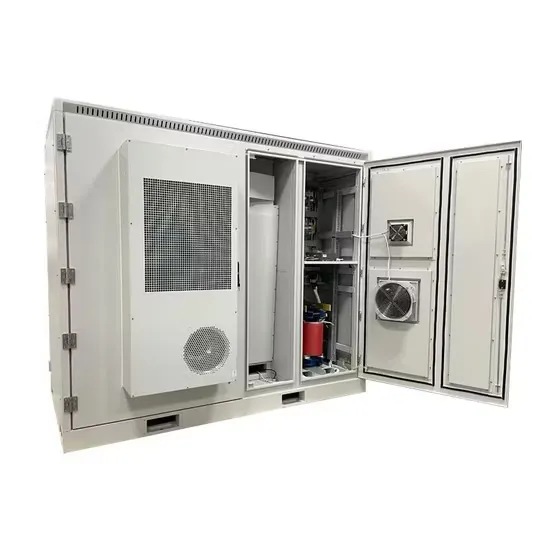
Communication base station grid-connected solar power
Cellular base stations powered by renewable energy sources such as solar power have emerged as one of the promising solutionsto these issues. This article presents an overview of the

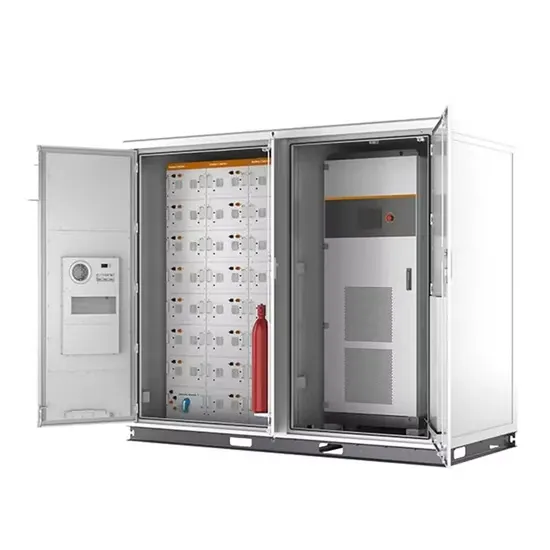
Inverter-based islanded microgrid: A review on
Jan 1, 2022 · In an inverter-based microgrid, grid-connected inverters are responsible for maintaining a stable operating point [112, 113]. Similar to a conventional power grid with

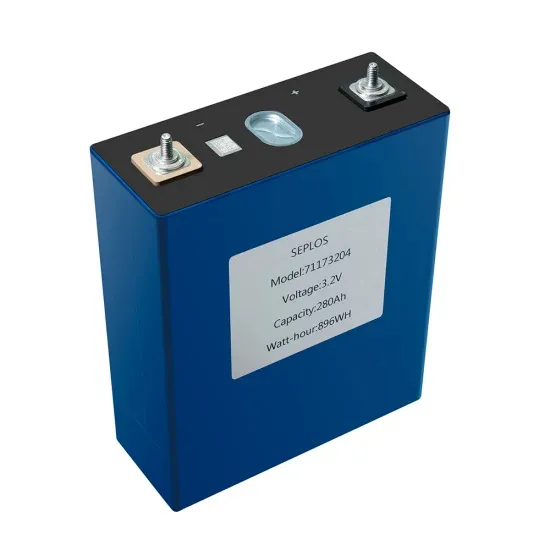
Control and Stability of Grid-Forming Inverters: A
Jun 30, 2024 · In contrast, grid-forming inverters (GFMIs) excel over GFLIs by offering features like standalone operation, frequency support, and adaptability in weak grid scenarios.
6 FAQs about [Communication base station inverter grid-connected operating frequency]
What is grid-forming inverter control strategy?
In the grid-forming inverter control strategy, the inverter can still be connected to the grid and realize frequency regulation when τ m reaches 4000 ms. In addition, the steady-state frequency and voltage are not affected by time delay. But too high delay is not conducive to the frequency stability of the system.
What is the difference between grid-following and grid-forming inverter control strategies?
In the grid-following inverter control strategy, the inverter cannot be connected to the grid when τ m reaches 1000 ms. In the grid-forming inverter control strategy, the inverter can still be connected to the grid and realize frequency regulation when τ m reaches 4000 ms.
Are grid-level coordinated inverter-based resources scalable and optimal frequency control?
This paper studies grid-level coordinated control of grid-forming (GFM) and grid-following (GFL) inverter-based resources (IBRs) for scalable and optimal frequency control.
Can a grid-forming inverter achieve power sharing without a communicati N link?
We show that the proposed contr l architectures achieve both power sharing without a communicati n link, and desirable passivity properties that can enhance the dynamic perf rm n e. Closed lo p stability of the grid-forming inverter with a dynamic load is also proven and simulations n advanced mod ls are carried out to validate the results.
Do grid-forming inverters have AC-side voltage regulation capability?
As grid-forming inverters are required to set the voltage of the network they form, it is important that they have AC-side voltage regulation capability. In the sequel, we propose a passivity-based proportional-integral controller (PIC).
Does grid-level coordinated control a mix of grid-forming and GFL inverter-based resources?
This paper studies the grid-level coordinated control of a mix of grid-forming (GFM) and grid-following (GFL) inverter-based resources (IBRs) for power system frequency regulation at scale.
Learn More
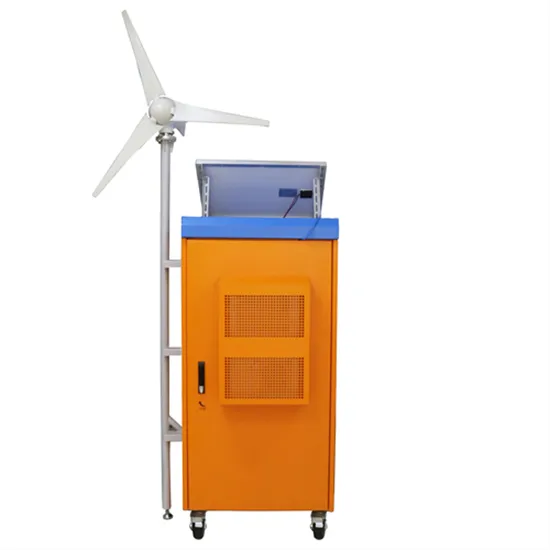
- Wind power communication base station inverter grid-connected energy storage cabinet
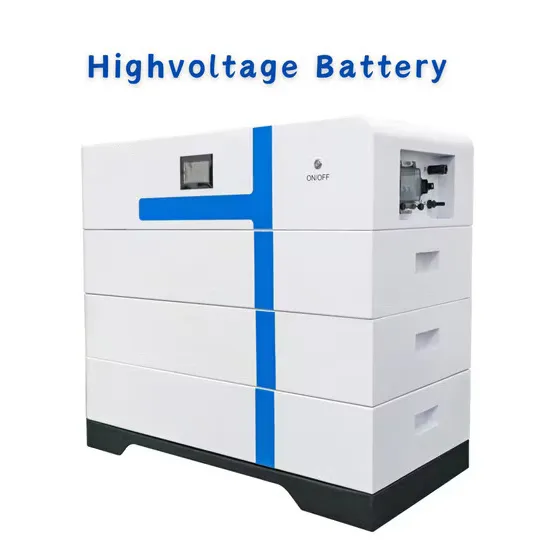
- Rooftop communication base station inverter grid-connected battery
- The communication base station inverter grid-connected network architecture includes
- East Asia Communication Base Station Inverter Grid-connected Photovoltaic Power Generation Quotation
- USA communication base station inverter grid-connected equipment processing
- Xia Communication Base Station Inverter Grid-connected Photovoltaic Power Generation System
- Communication base station inverter grid-connected battery detection principle
- Stockholm communication base station inverter grid-connected photovoltaic power generation system
- Pyongyang communication base station inverter grid-connected equipment processing
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
