
Light Pollution from Rooftop Solar Panels Solutions for
Summary: While rooftop photovoltaic (PV) panels support renewable energy adoption, their reflective surfaces contribute to urban light pollution. This article examines practical mitigation

How do solar panels cause light pollution?
Feb 21, 2024 · 1. Solar panels can contribute to light pollution primarily through reflective surfaces, 2. installation locations can disrupt local light ecology, 3.

Five key points of rooftop photovoltaic installation
Sep 26, 2024 · Large-scale photovoltaic arrays may cause visual pollution to urban landscapes and affect the quality of life of residents; at the same time, photovoltaic installations may also

Solar Panels: Light Pollution Or Clean Energy? | ShunWaste
May 27, 2025 · Overall, solar panels are a clean and renewable source of energy that does not contribute to light pollution. By providing an alternative to artificial lighting and reducing energy

Light pollution from rooftop solar panels
Photovoltaic solar panels are strong sources of a form of photopollution known as polarized light pollution(PLP,Horváth et al. 2009,2010a ). Do rooftop photovoltaic solar panels improve

Do Solar Panels Cause Light Pollution? The Glaring Truth
Picture this: you''ve just installed shiny new photovoltaic panels on your roof, ready to save the planet and your electricity bill. But then your neighbor complains about

Effects of solar photovoltaic technology on the environment
Aug 31, 2017 · Research institutions can address light pollution problems caused by solar panels by studying low-reflectivity photovoltaic glass. In addition, solar panels can affect the Earth''s

Photovoltaic panels as rooftop light pollution
About Photovoltaic panels as rooftop light pollution As the photovoltaic (PV) industry continues to evolve, advancements in Photovoltaic panels as rooftop light pollution have become critical to
The environmental factors affecting solar photovoltaic output
Feb 1, 2025 · Fourth, terrain factors like albedo and snow present mixed effects, with increased reflection boosting output but snow obstructing panels. Fifth, extreme weather like wildfires
What is the light pollution caused by photovoltaic panels
How do solar panels affect light pollution? Research institutions can address light pollution problems caused by solar panels by studying low-reflectivity photovoltaic glass. In addition,

Common Misconceptions Surrounding Glint and
May 17, 2021 · This is because most solar panels have a shiny surface or glass panel to protect it, whilst still letting light through. Shiny surfaces, such as

Rooftop photovoltaic solar panels warm up and cool down
Oct 7, 2024 · This study looks at the diurnal temperature fluctuations in Kolkata through a model that tests the influence of rooftop photovoltaic solar panels on urban surface energy budgets,

High Season for Shading and Pollution: How Do Leaves and
Comprehensive Guide to Hot Spot Risks in Solar Panels: From Bird Droppings and Leaf Shading to Power Loss and Encapsulation Degradation — Detection Methods, Risk Mitigation, and

DO SOLAR PANELS CREATE LIGHT POLLUTION
How do solar panels affect light pollution? Research institutions can address light pollution problems caused by solar panels by studying low-reflectivity photovoltaic glass. In addition,

Rooftop Photovoltaic Panels'' Evaluation for Houses in
Apr 30, 2023 · Due to air pollution and global warming, developed countries are preparing to use electric vehicles (EVs). Since fuel burns in the internal combustion engines, some harmful

Do photovoltaic solar panels cause light pollution
How do solar panels affect light pollution? Research institutions can address light pollution problems caused by solar panels by studying low-reflectivity photovoltaic glass. In addition,

Technical principles and prospects of distributed rooftop
Abstract: This paper will start from the concept of smart grid and green energy, analyze the advantages and applications of distributed rooftop photovoltaic (PV) power generation in the

Will Solar Modules Produce Light Pollution? | Raytech
Jan 11, 2021 · In fact, the visible light transmission coefficient of general tempered laminated glass is 9% ~ 11%, which is extremely hard to cause light pollution. The application of BIPV solar

Photovoltaic Power: Pollution Paradox? | ShunWaste
Mar 23, 2025 · Most PV panels produced today are made of single or multicrystalline silicon, and the production of high-purity polysilicon for solar cells has high energy requirements and

How can solar energy cause light pollution?
Sep 16, 2024 · 2. The first aspect to consider is how reflective surfaces of solar panels can redirect sunlight, thus causing light pollution in surrounding areas.

Air pollution and soiling implications for solar photovoltaic power
Sep 15, 2021 · Solar photovoltaic (PV) is a promising and highly cost-competitive technology for sustainable power supply, enjoying a continuous global installation growth supported by the

6 FAQs about [Will rooftop photovoltaic panels cause light pollution ]
How do solar panels affect light pollution?
Research institutions can address light pollution problems caused by solar panels by studying low-reflectivity photovoltaic glass. In addition, solar panels can affect the Earth’s exposure to light and thus indirectly affect the atmosphere.
How does Photovoltaic Glass affect the environment?
Photovoltaic glass produces a reflection effect with light reflectivity of approximately 4%, and its reflectance is maximum for infrared light with a wavelength greater than 1200 nm (Wang 2012). Reflected light on the surface of the glass causes light pollution. Light pollution can affect ecological balance.
What are the negative effects of solar photovoltaic system production?
The negative effects of solar photovoltaic system production include wastewater and waste gas pollutions, the representatives of which contain fluorine, chromium with wastewater and hydrogen fluoride, and silicon tetrachloride gas. Solar panels are also a source of light pollution.
What are the positive and negative aspects of solar photovoltaic technology?
The positive and negative aspects of solar photovoltaic technology, a novel technology, should be comprehensively considered. Solar energy is abundant, and its depletion is unlikely. The generation of solar photovoltaic systems does not cause any type of pollution and requires no energy consumption.
Why is solar photovoltaic not widely used?
Solar photovoltaic has not been widely utilized mainly because of the high electricity cost involved. Compared with traditional energy, solar energy has less impact on the environment. The global energy crisis also makes the application of solar photovoltaic technology particularly important.
How does green energy photovoltaic power generation affect the environment?
Improper disposal of solar cells that have reached the end of their service life harms the environment through the stench they produce and the damage they cause to the soil. So, the positive and negative effects of green energy photovoltaic power generation technology on the environment should be considered.
Learn More
- Do photovoltaic panels have voltage in weak light
- Yearly electricity generation of rooftop photovoltaic panels
- Insuring rooftop photovoltaic panels
- Steel Plant Rooftop Photovoltaic Panels
- Huawei Southern Europe rooftop photovoltaic panels
- Naypyidaw builds rooftop photovoltaic panels
- Maasai rural rooftop photovoltaic panels
- Rated light intensity of photovoltaic panels
- Manila rooftop photovoltaic panels
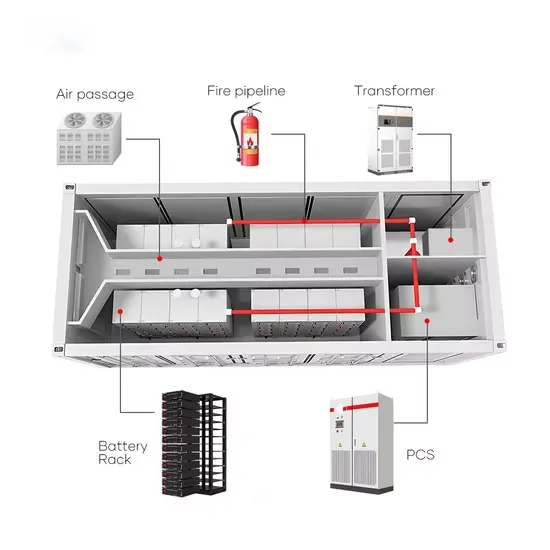
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
