
What Does Pv Mean In Solar Energy
Mar 15, 2025 · PV stands for photovoltaic, and in the context of solar energy, it refers to the technology used to convert sunlight into electricity. Photovoltaic systems consist of solar

What does it mean that photovoltaic power generation requires energy
Mar 29, 2020 · As the photovoltaic (PV) industry continues to evolve, advancements in What does it mean that photovoltaic power generation requires energy storage have become critical to

Photovoltaic cells convert solar energy into
May 13, 2015 · Photovoltaic is an adjective to identify everything that has to do with photovoltaic energy and the photovoltaic effect, more specifically. This

What does it mean that photovoltaic power generation
Mar 29, 2020 · What are the main features of solar photovoltaic (PV) generation? Abstract: This chapter presents the important features of solar photovoltaic (PV) generation and an overview

What does it mean that photovoltaic power generation
The use of PV as a main source requires energy storage systems or global distribution by high-voltage direct current power lines causing additional costs, or solar PV system is a power

Recent Facts about Photovoltaics in Germany
Jun 23, 2025 · In addition to the pure generation costs for electricity from RE, there are also power grids and the costs of building grid-serving storage and conversion capacities (e-mobility and
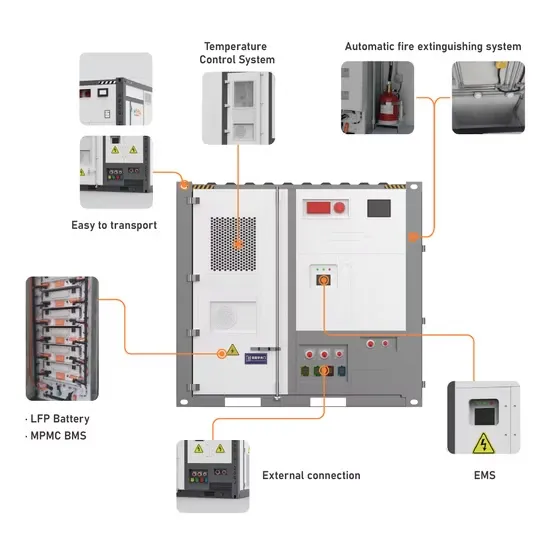
A review of energy storage technologies for large scale photovoltaic
Sep 15, 2020 · With this information, together with the analysis of the energy storage technologies characteristics, a discussion of the most suitable technologies is performed. In addition, this

How does photovoltaic power generation store
Aug 21, 2024 · Photovoltaic power generation stores energy in several key ways: 1. Through solar batteries that capture and store excess electricity generated

The Integration of Photovoltaics and Energy Storage: A
Nov 25, 2024 · Photovoltaics (PV) refers to the technology that converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels. Energy storage systems, on the other hand, store excess energy

what does photovoltaic mean › › Basengreen Energy
In conclusion, photovoltaic technology is a key driver of the transition to clean and sustainable energy sources. With ongoing research and development, the efficiency and affordability of

Solar power generation by PV (photovoltaic) technology: A review
May 1, 2013 · Solar power is the conversion of sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaic (PV), or indirectly using concentrated solar power (CSP). The research has been

Solar Photovoltaic Technology Basics | NREL
Mar 25, 2025 · Solar Photovoltaic Technology Basics Solar cells, also called photovoltaic cells, convert sunlight directly into electricity. Photovoltaics (often shortened as PV) gets its name

Photovoltaics (PV)
Apr 10, 2024 · I. What is Photovoltaics (PV)? Photovoltaics, commonly referred to as PV, is a technology that converts sunlight into electricity. This process involves the use of solar cells to
What does it mean that photovoltaic power generation
Abstract: This chapter presents the important features of solar photovoltaic (PV) generation and an overview of electrical storage technologies. The basic unit of a solar PV generation system

Solar power generation by PV (photovoltaic) technology: A
May 1, 2013 · Solar power is the conversion of sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaic (PV), or indirectly using concentrated solar power (CSP). The research has been
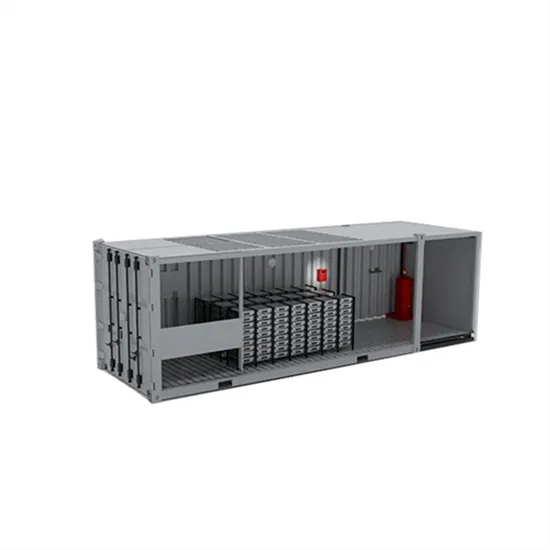

How does energy storage work with photovoltaics?
Energy storage at a photovoltaic plant works by converting and storing excess electricity generated by the photovoltaic plant, and then releasing it when demand increases or

Understanding Solar Photovoltaic System Performance
Feb 17, 2022 · This report presents a performance analysis of 75 solar photovoltaic (PV) systems installed at federal sites, conducted by the Federal Energy Management Program (FEMP) with
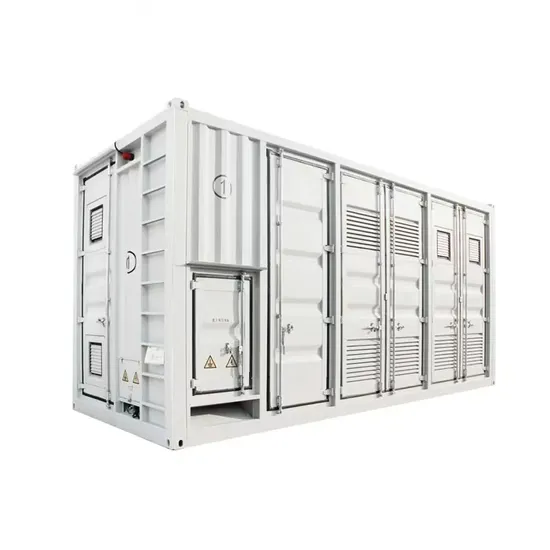

What does photovoltaic energy storage mean
What is a solar energy storage system? Solar storage systems store the excess energy produced by solar panels,making it available for use when sunlight is minimal or unavailable. These

Solar Power Generation and Energy Storage
2 days ago · Abstract: This chapter presents the important features of solar photovoltaic (PV) generation and an overview of electrical storage technologies. The basic unit of a solar PV
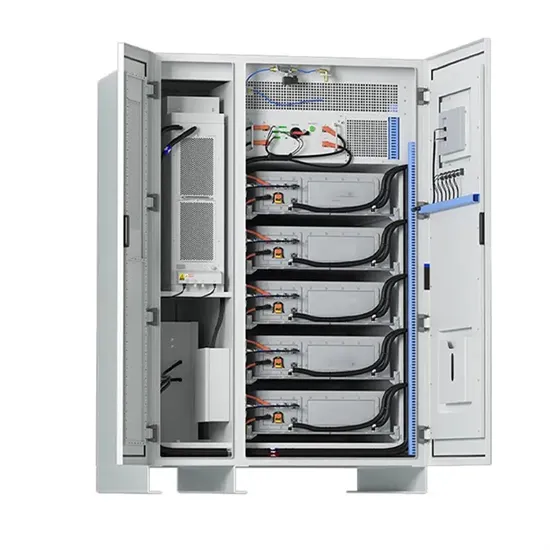

6 FAQs about [What does photovoltaic power generation and energy storage mean ]
What is the difference between photovoltaics and energy storage?
1. Introduction to Photovoltaics and Energy Storage Photovoltaics (PV) refers to the technology that converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels. Energy storage systems, on the other hand, store excess energy for later use, addressing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar power.
What is solar photovoltaic (PV) power generation?
Solar photovoltaic (PV) power generation is the process of converting energy from the sun into electricity using solar panels. Solar panels, also called PV panels, are combined into arrays in a PV system. PV systems can also be installed in grid-connected or off-grid (stand-alone) configurations.
What are the main features of solar photovoltaic (PV) generation?
This chapter presents the important features of solar photovoltaic (PV) generation and an overview of electrical storage technologies. The basic unit of a solar PV generation system is a solar cell, which is a P‐N junction diode. The power electronic converters used in solar systems are usually DC‐DC converters and DC‐AC converters.
What is the difference between solar PV and storage?
Both PV and storage technologies have seen rapid advancements: Solar PV: Modern solar panels are achieving efficiency levels of over 22%, making them more cost-effective than ever. Energy Storage: Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market, offering improved cycle life, energy density, and affordability.
Why is solar storage important?
Storage helps solar contribute to the electricity supply even when the sun isn’t shining. It can also help smooth out variations in how solar energy flows on the grid. These variations are attributable to changes in the amount of sunlight that shines onto photovoltaic (PV) panels or concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) systems.
Can solar energy be used as a energy storage system?
Existing compressed air energy storage systems often use the released air as part of a natural gas power cycle to produce electricity. Solar power can be used to create new fuels that can be combusted (burned) or consumed to provide energy, effectively storing the solar energy in the chemical bonds.
Learn More
- What are the photovoltaic power generation energy storage devices
- What energy storage is generally used for photovoltaic power generation
- Factory s own photovoltaic power generation and energy storage
- Astana Photovoltaic Power Generation and Energy Storage Solution
- 2kw photovoltaic power generation with 5 kWh of energy storage for home use
- Photovoltaic power generation and energy storage in Papua New Guinea
- Advantages of photovoltaic power generation and energy storage in Colombia
- One gigawatt of photovoltaic power generation and energy storage
- Skopje photovoltaic power generation cost with energy storage
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
