
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their
1 day ago · Related Post: Difference between Inverter & UPS – Uninterruptible Power Supply Different Types of Inverters Inverters are classified into many

Droop Control of Parallel Dual-Mode Inverters Used in
Abstract—Grid-connected and island control of parallel inverters used in micro grid based on a variety of micro-source were introduced in this paper. Micro-grid in the connected mode should

Microinverters: Everything You Need to Know in
Oct 4, 2022 · Microinverters vs String Inverters The major difference between string (or central) inverters and microinverters is the number of solar panels

SoC–Based Inverter Control Strategy for Grid-Connected
Jan 23, 2025 · By mimicking the behavior of the synchronous generators, droop control enables the decentralized and autonomous operation of multiple inverters in a microgrid (MG) [16]. The

Inverter-based islanded microgrid: A review on
Jan 1, 2022 · In the classification based on the mode of operation, inverters can be classified into three broad categories: autonomous inverters (supplies stable voltage and frequency to load),
Grid-Forming Inverters in a Microgrid: Maintaining Power
Jan 20, 2024 · This article presents an autonomous control architecture for grid-interactive inverters, focusing on the inverters providing power in a microgrid during utility

Micro Inverters: A Comprehensive Q&A Guid | Bonnen
Aug 26, 2024 · Bonnen Battery''s micro inverter experts answer all your questions. Find the best solar micro inverter for on-grid use, micro grid inverters.

On grid and Off Grid Micro Inverter in Solar Systems
Jan 15, 2025 · An off-grid micro inverter is a small inverter connected to individual solar panels in a system that operates independently of the main electricity grid. These inverters are

Can an Off Grid Inverter Work Without Batteries?
Nov 27, 2024 · Off-grid inverters can work without batteries, but this depends on the specific inverter model and application scenario. First of all, it should be clear that off-grid inverters are

hybrid inverter working with micro-inverters?
Nov 30, 2019 · Hello, I am thinking of buying a hybrid inverter in order to connect three strings (two half roofs and one flat garage) of around 5-8kW solar. Goal would be to use the electricity

Can I connect micro-inverter directly to a battery?
Mar 22, 2023 · I used a simmilar setup before I build my "big" PV installation. It was more for testing, but what I figured out was, that it made more sense to connect one PV module directly

Grid Connected Inverter Reference Design (Rev. D)
May 11, 2022 · High-efficiency, low THD, and intuitive software make this design attractive for engineers working on an inverter design for UPS and alternative energy applications such as

An Overview of the Roles of Inverters and Converters in
Feb 28, 2024 · Microgrids signify a transformative approach in energy distribution, pivoting away from traditional power grids toward a more decentralized, efficient, and sustainable model.

Grid-Forming Inverters for Grid-Connected Microgrids:
Mar 4, 2022 · Today, we have more and more renewable energy sources—photovoltaic (PV) solar and wind—connected to the grid by power electronic inverters. These inverter-based

Are micro inverters & battery backup compatible?
Nov 5, 2014 · With the growth in the use of micro inverters, I''m starting to get more and more emails asking: can micro inverters be used in off grid (or

Topologies and control strategies of multi-functional grid-connected
Aug 1, 2013 · Grid-connected inverters are key components of distributed generation systems (DGSs) and micro-grids (MGs), because they are effective interfaces for renewable and

Running Inverters in Parallel: A Comprehensive
Jul 14, 2023 · Additionally, running inverters in parallel can improve system reliability and redundancy. If one inverter fails, the others can continue to

6 FAQs about [Can micro grid-connected inverters be used ]
Can micro inverters be used in off grid solar power systems?
With the growth in the use of micro inverters, I’m starting to get more and more emails asking: can micro inverters be used in off grid (or hybrid) solar power systems? The short answer is yes they can! In fact a number of micro inverter battery backup systems are already operating here and abroad.
What is an inverter based microgrid?
An inverter-based MG consists of micro-sources, distribution lines and loads that are connected to main-grid via static switch. The inverter models include variable frequencies as well as voltage amplitudes. In an inverter-based microgrid, grid-connected inverters are responsible for maintaining a stable operating point [112, 113].
How do power converters work in a microgrid?
In a microgrid, with several distributed generators (DGs), energy storage units and loads, one of the most important considerations is the control of power converters. These converters implement interfaces between the DGs and the microgrid bus.
Is microgrid a good choice for power distribution systems?
Microgrid (MG) can improve the quality, reliability, stability and security of conventional distribution systems. Inverter based MGs are an appropriate, attractive and functional choice for power distribution systems. Inverters in a MG have multiple topologies that have been referenced in various literature.
Why are GS inverters not suitable for low-voltage microgrids?
the line impedance of a low-voltage microgrid has a large resistive component, thus P-ω and Q-U droop control is no longer suitable. the voltages at the PCs of each inverter are not completely equal, thus the GS inverters cannot share reactive power precisely.
Are U-droop grid-supporting inverters suitable for microgrids?
From the perspective of peer control, the ωU-droop grid-supporting invertershelp to realize microgrids’ plug and play function. Although being widely discussed in the technical literatures, it still lacks a sufficient practical control method andexisting control technologies need to be further studied and improved.
Learn More
- Can photovoltaic inverters be used indoors
- Micro inverters exported from Pakistan
- Micro grid-connected inverter connected to battery
- Grid-connected micro inverter supplier
- Huawei has photovoltaic grid-connected inverters
- What are the grid-connected projects for communication base station inverters in Tajikistan
- Grid-connected inverters are integrated into off-grid systems
- Micro inverters start exporting
- Temperature and humidity requirements for grid-connected inverters for communication base stations
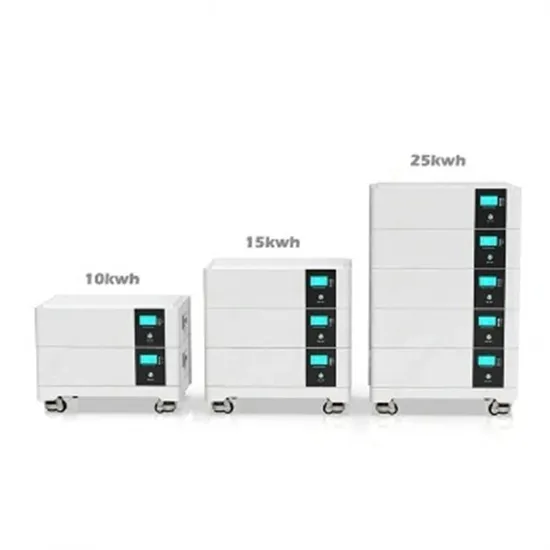
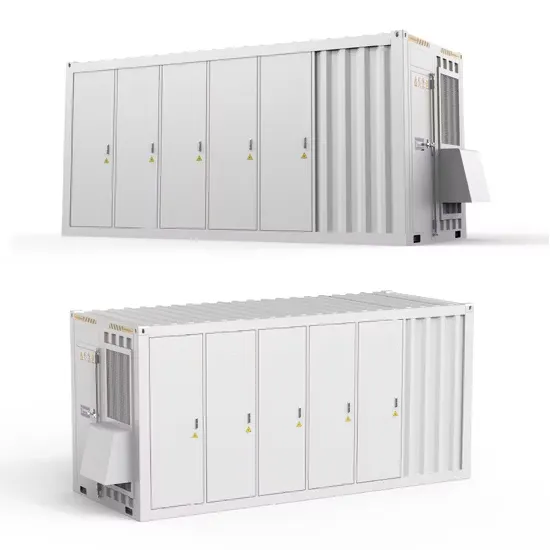
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
