
P/Q Control of Grid-Connected Inverters
Mar 25, 2021 · In photovoltaic grid-connected (GC) and DG systems, one of the objectives that the grid-connected inverters (GCI) is the control of current coming from the photovoltaic

Control of Grid-Connected Inverter | SpringerLink
May 17, 2023 · The control of grid-connected inverters has attracted tremendous attention from researchers in recent times. The challenges in the grid connection of inverters are greater as

fenrg-2022-1032993 1.
Nov 9, 2022 · Based on the microgrid operation structure, 5G base station and multi-objective problem algorithm, a multi-objective optimization operation model of microgrid access to 5G

Mobile base station site as a virtual power plant for grid
Mar 1, 2025 · The base station has a 3*25 Ampere (A) grid connection and several generations of mobile networks, including LTE & 5G in different frequency bands. The maximum theoretical

A comprehensive review of grid-connected solar
Jun 1, 2023 · The various control techniques of multi-functional grid-connected solar PV inverters are reviewed comprehensively. The installed capacity of solar photovoltaic (PV) based

Synchronization in electric power networks with inherent
May 5, 2022 · In future power networks dominated by grid-forming inverters, new concepts such as adaptive protection that follows the grid inertia to adjusts its settings in real-time, and

Solar inverters and inverter solutions for power generation
Mar 13, 2020 · The ABB inverter station is a compact turnkey solution designed for large-scale solar power generation. It houses all equipment that is needed to rapidly connect ABB central

Dynamic phasor-based hybrid simulation for multi-inverter grid
May 19, 2023 · To realize the efficient transient simulation of a grid-connected power generation system based on multiple inverters,this paper proposes a hybrid simulation method integrating

Grid-Forming Inverters: Project Demonstrations and Pilots
Feb 23, 2024 · Power system operators around the world are pushing the limits of integrating inverter-based resources (IBRs) to very high levels, approaching 100% instantaneou

A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
Oct 1, 2018 · In this paper global energy status of the PV market, classification of the PV system i.e. standalone and grid-connected topologies, configurations of grid-connected PV inverters,
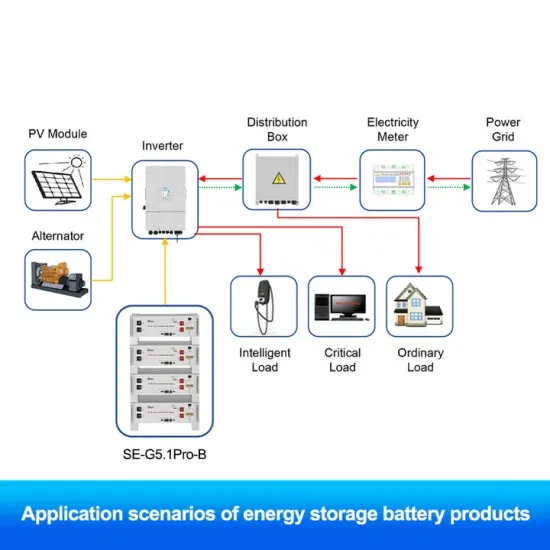
Hybrid compatible grid forming inverters with coordinated
Aug 16, 2025 · A recent study 34 proposed a grid-forming voltage-source inverter for interfacing hybrid wind–solar systems with weak grids, demonstrating its effectiveness in voltage

Review of Advances in Grid-Connected Inverters and Control
Nov 28, 2024 · A functional comparison between grid-forming inverters (GFMI) and grid-following inverters (GFLI) is conducted in order to demonstrate the potential of grid-forming inverter

Environmental Impact Assessment of Power Generation
Hybrid power systems were used to minimize the environmental impact of power generation at GSM (global systems for mobile communication) base station sites. This paper presents the

SoC–Based Inverter Control Strategy for Grid-Connected
Jan 23, 2025 · This benchmark is a robust foundation for investigating control features of grid-connected inverters in BESS applications [40, 41]. CIGRE''s primary focus on low-voltage

(PDF) Critical review on various inverter
Feb 22, 2021 · This review would be helpful for researchers in this field to select a most feasible inverter for their application, as this study reviews considerable

GRID CONNECTED PV SYSTEMS WITH BATTERY ENERGY
May 22, 2023 · This section applies to any inverter that interconnects with a battery system. This includes PV battery grid connect inverters, battery grid connect inverters and stand-alone

Dispatching Grid-Forming Inverters in Grid-Connected
Aug 1, 2024 · GFM inverters usually use droop control to automatically share power with other GFM sources (inverters and synchronous generators) and follow the change in the load

Communication Base Station Innovation Trends | HuiJue
Rethinking Infrastructure for the 5G-Advanced Era As global mobile data traffic surges 35% annually, communication base stations face unprecedented demands. Can traditional tower

Passivity-Based Control for the Stability of Grid-Forming
Feb 15, 2025 · Existing grid-connected inverters encounter stability issues when facing nonlinear changes in the grid, and current solutions struggle to manage complex grid environments

GRID-CONNECTED PV SYSTEMS
Apr 26, 2021 · The NEC requirements are provided as notes where appropriate. Figure 1 shows a typical interconnection of a grid connected PV system while Figures 2 and 3 are typical wiring
STEVAL-ISV002V1, STEVAL-ISV002V2 3 kW grid
It consists of a high frequency isolated input power section performing DC-DC conversion and an inverter section capable of delivering sinusoidal current of 50 Hz to the grid. The system

Grid-Connected/Islanded Switching Control Strategy for
This strategy effectively mitigated transient voltage and current surges during mode transitions. Consequently, seamless and efficient switching between grid-connected and island modes

Support functions and grid-forming control on grid connected inverters
Aug 6, 2024 · Grid-connected inverters (GCIs) may be operated in voltage-control mode using the so-called grid-forming (GFM) strategies. This control technique enables active and reactive

Dynamic phasor-based hybrid simulation for multi-inverter grid
Apr 1, 2023 · To realize the efficient transient simulation of a grid-connected power generation system based on multiple inverters, this paper proposes a hybrid simulation method

Grid-connected photovoltaic power systems: Technical and
Jan 1, 2010 · Grid interconnection of PV systems is accomplished through the inverter, which convert dc power generated from PV modules to ac power used for ordinary power supply to
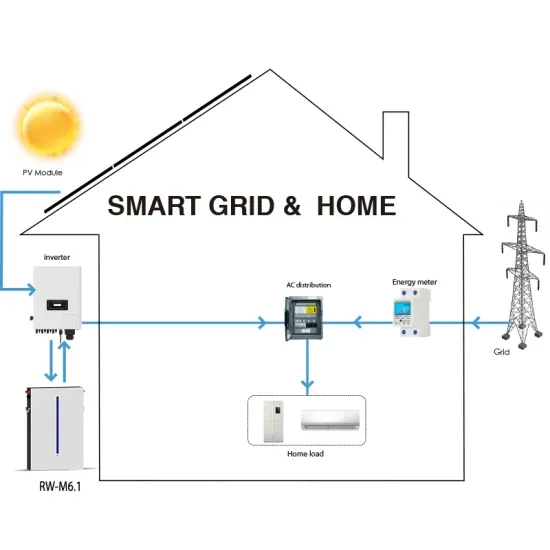
6 FAQs about [Global communication base station inverter grid-connected field]
Can grid-forming inverters improve power system stability and resilience?
A functional comparison between grid-forming inverters (GFMI) and grid-following inverters (GFLI) is conducted in order to demonstrate the potential of grid-forming inverter technologies for enhancing power system stability and resilience.
Which mode of VSI is preferred for grid-connected PV systems?
Between the CCM and VCM mode of VSI, the CCM is preferred selection for the grid-connected PV systems. In addition, various inverter topologies i.e. power de-coupling, single stage inverter, multiple stage inverter, transformer and transformerless inverters, multilevel inverters, and soft switching inverters are investigated.
What is a grid-forming inverter?
Grid-forming inverters maintain an internal voltage phasor, enabling rapid response to changes. Understanding grid-forming versus grid-following controls is essential for optimizing grid reliability. For more insights, download our white paper.
What is a power electronic based inverter?
In both standalone or grid-connected PV systems, power electronic based inverter is the main component that converts the DC power to AC power, delivering in this way the power to the AC loads or electrical grid.
What are the control structures for single-phase grid-connected inverters?
The control structures for single-phase grid-connected inverters are mostly classified into three categories: (1) control structure for single-phase inverter with DC-DC converter, (2) control structure for single-phase inverter without DC-DC converter, and (3) control structure based on Power Control Shifting Phase (PCSP).
What are the requirements for grid-connected inverters?
The requirements for the grid-connected inverter include; low total harmonic distortion of the currents injected into the grid, maximum power point tracking, high efficiency, and controlled power injected into the grid. The performance of the inverters connected to the grid depends mainly on the control scheme applied.
Learn More
- Samoa communication base station inverter grid-connected construction project bidding
- Communication base station inverter grid-connected behavior example
- Bahrain communication base station inverter grid-connected module
- Communication base station inverter grid-connected front end
- Brad Communication Base Station Inverter Grid-Connected
- The grid-connected inverter of a communication base station should be 7MWh
- Communication base station inverter grid-connected pam
- What is the quota for adding panels to the grid-connected inverter of a communication base station
- Communication base station inverter grid-connected engineering quantity list
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing explosive growth, with demand increasing by over 250% in the past two years. Containerized energy storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial and industrial storage deployments worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and tax incentives that reduce total project costs by 18-28%. Europe follows closely with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 65% compared to traditional built-in-place systems. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing scale reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are adopting industrial storage solutions for peak shaving and backup power, with typical payback periods of 2-4 years. Major commercial projects now deploy clusters of 15+ systems creating storage networks with 80+MWh capacity at costs below $270/kWh for large-scale industrial applications.
Industrial Energy System Innovations & Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving industrial energy storage performance while reducing costs. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal operating conditions with 45% less energy consumption, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $85/kWh to $40/kWh since 2023. Smart integration features now allow multiple industrial systems to operate as coordinated energy networks, increasing cost savings by 30% through peak shaving and demand charge management. Safety innovations including multi-stage fire suppression and thermal runaway prevention systems have reduced insurance premiums by 35% for industrial storage projects. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple system additions at just $200/kWh for incremental capacity. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial and industrial projects typically achieving payback in 3-5 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (1-2MWh) starting at $330,000 and large-scale systems (3-6MWh) from $600,000, with volume discounts available for enterprise orders.
